TECHNOLOGY
Global Technology Solutions: A Practical, Real-World Guide for Modern Organizations

If you run, manage, or advise a business today, you’ve probably felt it already: the quiet pressure that everything must work everywhere, all the time. Customers expect instant responses across borders. Teams collaborate from different time zones. Data moves faster than regulations can keep up. And a single technology failure in one region can ripple across an entire organization.
This is exactly why global technology solutions have moved from “nice to have” to mission-critical.
This guide is for founders scaling internationally, IT leaders managing distributed systems, operations managers juggling vendors across continents, and decision-makers who are tired of fragmented tools that don’t talk to each other. It’s also for anyone who suspects that their current tech stack is holding them back—but isn’t sure where to start fixing it.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand what global technology solutions really mean in practice, how they solve real operational problems, where they succeed or fail in the real world, and how to implement them without wasting budget or burning out your team. No buzzwords. No theory-only frameworks. Just hard-earned insights from the field.
Understanding Global Technology Solutions (From Beginner to Expert)
At its core, global technology solutions refer to integrated technology systems designed to operate consistently across multiple countries, regions, and regulatory environments. But that definition barely scratches the surface.
Think of it like building a global transportation network. Roads, traffic laws, fuel standards, and vehicles vary by country—but the goal is seamless movement from point A to point B anywhere in the world. Technology works the same way. The systems must adapt locally while remaining unified globally.
For beginners, global technology solutions often start with basics: cloud-based tools accessible worldwide, standardized communication platforms, and centralized data storage. These are the foundations. Without them, international growth quickly turns chaotic.
As organizations mature, the focus shifts to integration and resilience. Systems must sync across regions in real time, comply with local regulations automatically, and maintain uptime even when parts of the world go offline. This is where architecture, governance, and process design become just as important as software.
At an expert level, global technology solutions become strategic assets. They enable rapid market entry, data-driven decisions across regions, and operational consistency without sacrificing local flexibility. Companies at this stage don’t ask, “Can our tech support global growth?” They ask, “How can our technology create a global competitive advantage?”
The Real Benefits and Use Cases of Global Technology Solutions
The biggest misconception about global technology solutions is that they’re only for massive corporations. In reality, businesses of all sizes benefit—just in different ways.
For startups and scale-ups, the benefit is speed. A unified technology backbone allows rapid expansion into new markets without rebuilding systems from scratch. Payments, customer support, analytics, and collaboration tools can be extended globally with minimal friction.
Mid-sized companies see efficiency gains. Before global solutions, teams often operate in silos—different tools, different processes, different data. After implementation, reporting becomes unified, workflows standardize, and leadership finally sees the full picture instead of fragmented regional snapshots.
Large enterprises benefit from risk reduction and optimization. Centralized monitoring improves security. Standardized platforms reduce vendor sprawl. Compliance becomes manageable instead of reactive. Most importantly, leadership can make strategic decisions based on global data rather than regional guesswork.
Real-world use cases span industries:
- Retail brands using unified commerce platforms to synchronize inventory across continents
- Healthcare organizations securing patient data while supporting cross-border research
- Financial services firms maintaining compliance while offering real-time global services
- Manufacturing companies optimizing supply chains with live global data
The “before” state is usually messy: duplicated tools, inconsistent data, delayed decisions. The “after” state is clarity, control, and confidence.
A Step-by-Step Practical Guide to Implementing Global Technology Solutions
Implementing global technology solutions isn’t about buying one big system and flipping a switch. It’s a structured process that rewards patience and planning.
Start with a global audit. Map every system currently in use, region by region. You’ll almost always find redundancies, outdated tools, and shadow IT that leadership didn’t even know existed. This step alone often reveals immediate cost-saving opportunities.
Next, define non-negotiables. These are the standards every region must follow—security protocols, data structures, communication tools, and reporting formats. Without clear guardrails, “global” quickly devolves into “loosely connected.”
Then design for local flexibility. Global solutions fail when they ignore local realities. Time zones, languages, regulations, and cultural workflows matter. Build modular systems that allow regional customization without breaking the core architecture.
Roll out in phases. Start with one or two regions, refine the approach, then scale. This reduces risk and builds internal champions who can support adoption elsewhere.
Finally, invest in governance and training. Technology doesn’t manage itself. Clear ownership, documented processes, and continuous education ensure the system evolves instead of decaying.
Tools, Comparisons, and Expert Recommendations
Choosing tools for global technology solutions is less about brand names and more about fit. The best tools are the ones your teams actually use correctly.
Free tools work well for early-stage organizations testing international collaboration. They offer flexibility but often lack advanced security and integration capabilities.
Paid, professional platforms provide scalability, compliance support, and reliability—but require disciplined implementation. Without proper configuration, they become expensive clutter.
Beginner-friendly tools prioritize ease of use and quick setup. Advanced platforms emphasize customization, automation, and analytics. Lightweight tools are ideal for focused tasks, while enterprise solutions handle complex, interconnected workflows.
Expert recommendation: prioritize interoperability over features. A slightly less powerful tool that integrates cleanly across regions will outperform a feature-rich platform that creates data silos.



Common Mistakes (and How to Avoid Them)
One of the most common mistakes is assuming technology alone solves global complexity. It doesn’t. Poor processes simply scale into bigger problems.
Another frequent error is over-standardization. Forcing identical workflows across vastly different regions often leads to workarounds and resistance. Balance consistency with autonomy.
Underestimating change management is another pitfall. Teams don’t resist technology—they resist disruption without context. Clear communication and phased rollouts prevent backlash.
Security is often addressed too late. Global systems expand the attack surface. Build security into the foundation, not as an afterthought.
Finally, many organizations fail to revisit their architecture. Global technology solutions are living systems. Regular reviews keep them aligned with business goals.
The Strategic Value of Global Technology Solutions in 2026 and Beyond
Looking ahead, global technology solutions are becoming less about infrastructure and more about intelligence. Automation, analytics, and real-time insights are turning technology platforms into decision engines.
Organizations that invest now gain agility later. They respond faster to market changes, adapt to regulations with less friction, and attract global talent who expect modern systems.
The gap between companies with cohesive global solutions and those without will continue to widen. This isn’t a trend—it’s a structural shift in how modern organizations operate.

Conclusion: Turning Global Technology Solutions into a Competitive Advantage
Global technology solutions aren’t about chasing trends or copying what big companies do. They’re about building a technology foundation that supports how your organization actually works—across borders, cultures, and time zones.
When implemented thoughtfully, they reduce chaos, unlock growth, and create resilience. When rushed or poorly governed, they amplify problems.
The opportunity is clear: design global systems that are human-friendly, adaptable, and aligned with real business needs. Start small, think strategically, and treat technology as a long-term investment—not a one-time project.
If you do that, global technology solutions won’t just support your growth. They’ll define it.
FAQs
They are technology systems designed to work consistently across multiple countries while adapting to local needs.
Yes, especially if they plan to scale internationally or work with distributed teams.
It varies, but phased rollouts typically span several months to a year.
Not necessarily. They often reduce long-term costs by eliminating redundancies.
Retail, finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and tech-driven services see the biggest gains.
TECHNOLOGY
Nuclear Medicine Technology: How It Quietly Became One of the Most Powerful Tools in Modern Healthcare
If you’ve ever watched a doctor spot disease before symptoms even appear, there’s a good chance nuclear medicine technology was working quietly behind the scenes. Unlike many medical tools that react to problems once they’re visible, this field specializes in seeing what’s happening beneath the surface—at the cellular and molecular level—often months or even years earlier.
That early insight is exactly why nuclear medicine technology has become so important right now. Healthcare systems are under pressure to diagnose faster, treat more precisely, and avoid unnecessary procedures. Patients want answers sooner, with less guesswork and fewer invasive tests. Clinicians want data they can trust when decisions carry life-altering consequences.
This article is for clinicians, healthcare administrators, medical students, technologists, and even curious patients who want to understand how modern diagnostics really work. We’ll unpack how nuclear medicine technology functions, where it shines in real-world settings, and how it’s evolving from a specialized imaging niche into a core pillar of precision medicine.
By the end, you’ll understand not just what nuclear medicine technology is, but why hospitals invest millions in it, why oncologists rely on it daily, and why its future looks far bigger than most people realize.
Understanding Nuclear Medicine Technology From the Ground Up
At its core, nuclear medicine technology is about function, not form. Traditional imaging methods like X-rays or CT scans show structure—bones, organs, tumors once they’re large enough to see. Nuclear medicine, on the other hand, shows how tissues behave.
The process begins with a radiopharmaceutical, often called a tracer. This is a compound designed to mimic a natural substance in the body—like glucose or iodine—tagged with a tiny amount of radioactive material. Once injected, inhaled, or swallowed, it travels through the body and concentrates in specific organs or tissues.
Here’s where the magic happens. As the tracer decays, it emits gamma rays or positrons. Specialized cameras detect this energy and convert it into images that reveal metabolic activity. Areas of high uptake might indicate cancer, inflammation, or abnormal organ function long before structural damage occurs.
Think of it like checking a car’s engine diagnostics instead of waiting for smoke to appear. Nuclear medicine technology tells clinicians how the engine is running, not just what it looks like from the outside.
As practitioners gain experience, they move beyond simple detection into interpretation—correlating uptake patterns with disease stages, treatment response, and prognosis. That’s where beginner understanding turns into expert insight, and why training and context matter so much in this field.
The Science Behind PET, SPECT, and Hybrid Imaging
Two workhorses dominate nuclear medicine technology: PET and SPECT imaging. Each has its own strengths, and understanding the difference explains why both still matter.
PET imaging uses positron-emitting tracers. When a positron meets an electron, they annihilate each other, producing two photons that travel in opposite directions. Detectors capture these signals with remarkable precision, allowing clinicians to map metabolic activity with high resolution. This makes PET invaluable in oncology, neurology, and cardiology.
SPECT imaging, by contrast, relies on gamma-emitting tracers. The technology is slightly older, but still incredibly useful. SPECT cameras rotate around the patient, building a 3D image of tracer distribution. It’s widely used for cardiac perfusion studies, bone scans, and thyroid imaging.
The real leap forward came with hybrid systems. PET/CT and SPECT/CT combine functional and anatomical imaging in one session. The CT component provides structural context, while the nuclear scan reveals activity. This fusion reduces ambiguity and increases diagnostic confidence.
Manufacturers like Siemens Healthineers and GE Healthcare have refined these systems to the point where workflow efficiency and image quality continue to improve year after year.
Real-World Benefits and Clinical Use Cases That Matter
The true value of nuclear medicine technology becomes clear when you see how it changes outcomes in real clinical settings. Oncology is the most obvious example. PET scans help stage cancer accurately, determine whether a tumor is active or dormant, and assess whether treatment is working after just a few cycles.
Before nuclear imaging, many patients endured months of therapy before anyone knew if it was effective. Today, clinicians can pivot quickly, sparing patients unnecessary side effects and lost time.
Cardiology offers another powerful use case. Myocardial perfusion imaging identifies areas of reduced blood flow, helping cardiologists decide who needs intervention and who can be managed medically. This targeted approach reduces unnecessary catheterizations and lowers overall risk.
Neurology also benefits enormously. PET imaging can differentiate between types of dementia, identify seizure foci, and support early diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease. That early clarity can shape treatment plans and family decisions in profound ways.
Across these scenarios, the tangible outcomes are consistent: faster diagnosis, more precise treatment, lower long-term costs, and improved patient confidence. It’s not just about better images—it’s about better decisions.
A Step-by-Step Look at How Nuclear Medicine Works in Practice
From the outside, a nuclear medicine exam might seem simple. In reality, it’s a carefully orchestrated process where each step matters.
First comes patient preparation. Depending on the study, patients may need to fast, avoid certain medications, or hydrate well. These steps directly affect tracer distribution and image accuracy.
Next is radiopharmaceutical selection. The choice depends on the clinical question. For example, fluorodeoxyglucose is commonly used in oncology because it highlights glucose-hungry cancer cells. Cardiac studies use tracers optimized for myocardial uptake.
After administration, there’s a waiting period. This allows the tracer to distribute and localize appropriately. Timing here is critical; image too early or too late, and the diagnostic value drops.
Imaging itself requires precision positioning and calibration. Technologists ensure patient comfort while minimizing motion, which can degrade results. The acquired data then goes through reconstruction algorithms that turn raw signals into interpretable images.
Finally comes interpretation. Nuclear medicine physicians correlate scan findings with clinical history, lab results, and other imaging. This synthesis is where experience truly shows, transforming colorful images into actionable insights.
Tools, Systems, and Expert Recommendations From the Field
Not all nuclear medicine technology is created equal. Entry-level systems may suit smaller clinics with limited case complexity, while large academic centers require high-throughput, research-grade equipment.
PET/CT systems vary in detector sensitivity, scan speed, and software sophistication. Advanced models reduce radiation dose while improving resolution—an important balance as patient safety remains paramount.
Software tools are just as critical. Image fusion, quantitative analysis, and AI-assisted interpretation are becoming standard. These tools don’t replace clinicians, but they enhance consistency and flag subtle changes that might otherwise be missed.
From an expert perspective, the best choice depends on case mix, staffing, and long-term strategy. Overinvesting can strain budgets, while underinvesting limits diagnostic capability. Seasoned administrators prioritize scalability, service support, and training resources alongside headline specs.
Common Mistakes and How Experienced Teams Avoid Them
One of the most common mistakes in nuclear medicine technology is underestimating preparation. Poor patient prep leads to non-diagnostic scans, repeat exams, and unnecessary radiation exposure.
Another frequent issue is misinterpretation due to lack of clinical context. Uptake patterns can be misleading without understanding the patient’s history, recent treatments, or comorbidities. This is why multidisciplinary communication is essential.
Equipment calibration and quality control also trip up inexperienced teams. Small technical issues can snowball into systemic inaccuracies if not caught early. Experienced departments invest heavily in routine checks and continuous education.
Finally, some organizations treat nuclear medicine as a standalone service rather than an integrated diagnostic partner. The most successful programs embed nuclear imaging into care pathways, ensuring findings directly inform clinical decisions.
Regulation, Safety, and Ethical Considerations
Radiation safety is central to nuclear medicine technology. While doses are generally low and carefully controlled, strict protocols govern handling, administration, and disposal of radioactive materials.
Organizations like the International Atomic Energy Agency and the World Health Organization provide guidelines that shape best practices worldwide. These standards protect patients, staff, and the environment.
Ethical considerations also come into play. Clear communication about risks, benefits, and alternatives builds trust. Informed consent isn’t just a form—it’s a conversation that respects patient autonomy and understanding.
The Future of Nuclear Medicine Technology
Looking ahead, nuclear medicine technology is moving toward personalization. New tracers target specific receptors, enzymes, or genetic markers, allowing imaging tailored to individual biology.
Theranostics—a combination of therapy and diagnostics—represents a major frontier. The same molecule used to detect disease can deliver targeted treatment, closing the loop between diagnosis and therapy.
Artificial intelligence will further refine image interpretation, workflow efficiency, and predictive analytics. Rather than replacing experts, AI will act as a second set of eyes, reducing variability and enhancing confidence.
As these advances converge, nuclear medicine will shift from a supporting role to a central driver of precision healthcare.
Conclusion: Why This Technology Deserves Your Attention
Nuclear medicine technology isn’t flashy, and it rarely makes headlines. Yet its impact on modern healthcare is profound. By revealing disease processes at their earliest stages, it empowers clinicians to act decisively and patients to make informed choices.
Whether you’re a practitioner refining your skills, an administrator planning investments, or a patient seeking understanding, this field offers clarity where uncertainty once ruled. The more you appreciate how it works, the more you see why it has become indispensable.
The future belongs to medicine that understands function, not just form—and nuclear medicine technology is leading that charge.
FAQs
It focuses on how organs and tissues function rather than just their structure, enabling earlier and more precise diagnosis.
Yes. Radiation doses are carefully controlled and generally comparable to or lower than many CT exams.
Depending on the study, the entire process may take a few hours, though imaging itself is often under an hour.
In many cases, yes. Functional changes often appear before structural tumors are visible on conventional imaging.
Specialized education in radiopharmaceuticals, imaging physics, and clinical interpretation is essential, along with ongoing certification.
TECHNOLOGY
Carbon Capture Technology: How It Works, Why It Matters, and What Actually Delivers Results

A few years ago, most conversations about climate change felt abstract. Distant. Someone else’s problem. Today, that illusion is gone.
Energy prices swing wildly. Governments tighten emissions rules. Corporations face investor pressure they didn’t see coming five years ago. And communities feel the physical effects—heat, floods, air quality—in ways that can’t be ignored.
That’s why carbon capture technology has moved from academic white papers into boardrooms, factory floors, and national energy strategies.
This article is written for people who don’t want hype, buzzwords, or theoretical promises. It’s for decision-makers, engineers, sustainability leads, policy professionals, and curious readers who want to understand:
Why carbon capture technology is being taken seriously right now
Where it actually works—and where it doesn’t
What real-world deployment looks like
How to evaluate tools, systems, and strategies without getting burned
By the end, you’ll have a grounded, experience-based understanding of carbon capture technology—what it can realistically do, how it’s implemented step by step, and how to avoid the mistakes that quietly derail projects.
No fluff. No preaching. Just clarity.
What Carbon Capture Technology Actually Is (From First Principles to Real Systems)
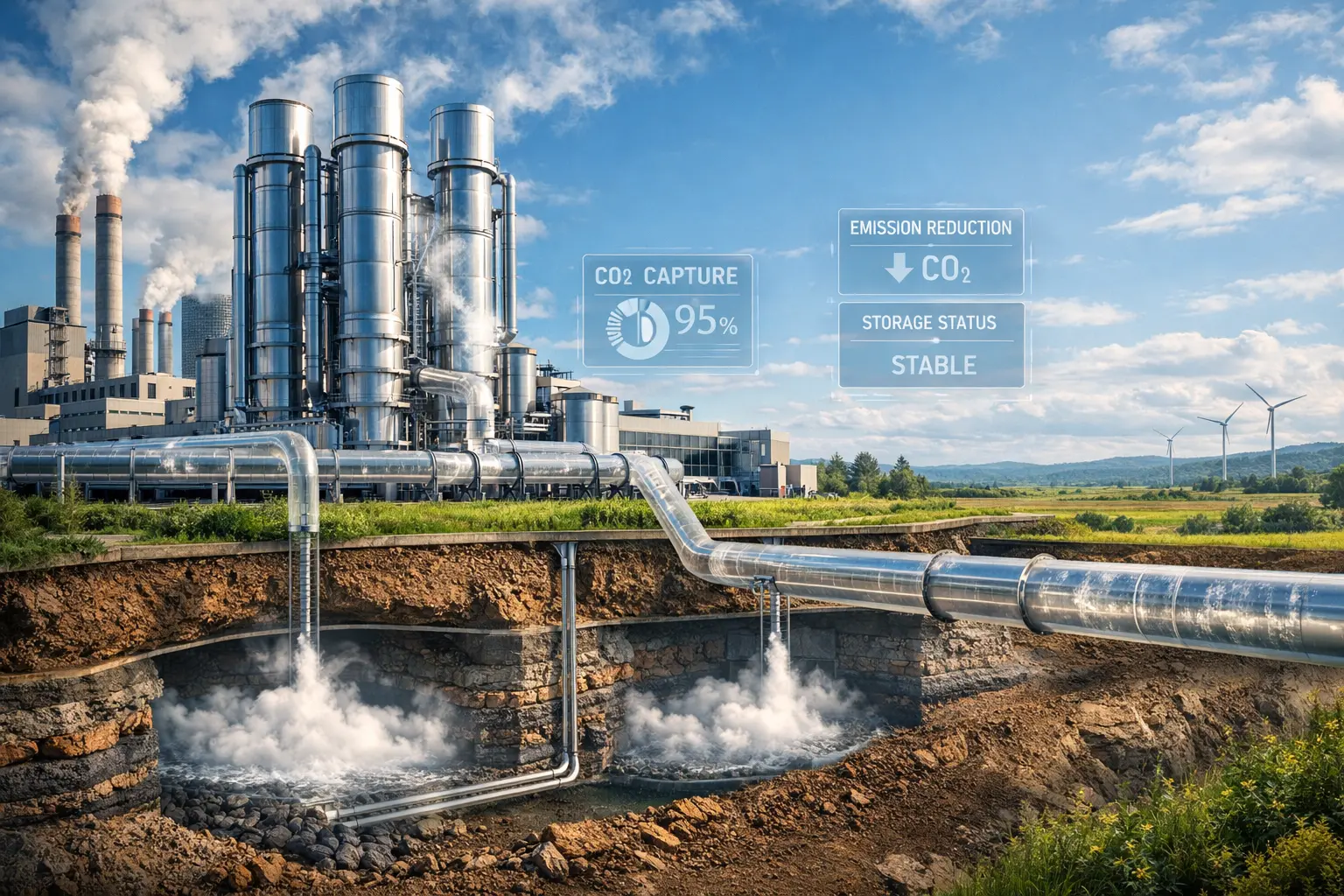
At its core, carbon capture technology is about intercepting carbon dioxide before it reaches the atmosphere—or pulling it back out after it’s already there—and managing it responsibly.
A simple analogy helps.
Think of industrial emissions like smoke from a fireplace. Carbon capture technology is the equivalent of installing a high-efficiency chimney filter, then deciding whether to store the collected soot safely, reuse it, or neutralize it entirely.
But unlike smoke, carbon dioxide is invisible, chemically stable, and produced at massive scale. Capturing it requires precision engineering, chemistry, and infrastructure.
There are three main stages involved:
Capture
Transport
Storage or utilization
Capture is where most of the technical complexity lives. This is where CO₂ is separated from flue gases or ambient air. Depending on the method, this might involve solvents, membranes, solid sorbents, or mineral reactions.
Transport comes next. Once captured, CO₂ must be compressed and moved—usually via pipelines, ships, or trucks—to its destination.
Finally, the carbon is either stored underground in geological formations or reused in industrial processes like fuel synthesis, building materials, or chemical manufacturing.
What’s important to understand early is that carbon capture technology isn’t one thing. It’s a family of approaches, each with trade-offs depending on scale, cost, location, and industry.
And that distinction matters more than most headlines admit.
Why Carbon Capture Technology Matters Right Now (Not in 2050)
Timing is everything.
Carbon capture technology isn’t gaining traction because it’s trendy—it’s gaining traction because other options alone aren’t moving fast enough.
Renewables are scaling, but not instantly
Electrification is accelerating, but not universal
Heavy industries still rely on combustion processes
Steel, cement, chemicals, refining, and power generation account for a huge share of global emissions—and many of these processes cannot simply “go electric” overnight.
Carbon capture technology offers something rare in climate strategy: a way to reduce emissions without rebuilding entire industrial systems from scratch.
That’s why governments are funding it. Why oil and gas companies are investing. Why industrial giants are piloting projects even amid skepticism.
It’s not a silver bullet. But it is a bridge—one that buys time while deeper transitions take place.
Ignoring it doesn’t make emissions disappear. Deploying it intelligently can.
Real-World Benefits and Use Cases That Actually Matter
The strongest case for carbon capture technology isn’t ideological—it’s practical.
The biggest beneficiaries tend to fall into three categories.
Industries with unavoidable process emissions
Regions with existing fossil infrastructure
Companies facing immediate regulatory pressure
In cement manufacturing, for example, over half of emissions come from chemical reactions, not fuel combustion. Even 100% renewable energy wouldn’t eliminate them. Carbon capture technology directly addresses that gap.
In oil- and gas-producing regions, existing pipelines, geological storage sites, and technical expertise make deployment far more feasible than starting from zero.
For corporations, carbon capture technology can mean:
Compliance without shutdowns
Preserving jobs while lowering emissions
Creating monetizable carbon products
Reducing long-term regulatory risk
Before deployment, companies often face escalating carbon taxes, investor scrutiny, and public pressure. After deployment, emissions profiles improve, compliance costs stabilize, and future planning becomes easier.
The difference isn’t theoretical—it shows up on balance sheets.
How Carbon Capture Technology Is Implemented Step by Step
Successful deployment doesn’t start with equipment. It starts with context.
Step one is emissions assessment. You need to know where CO₂ is produced, at what concentration, and in what volumes. High-concentration streams are dramatically easier and cheaper to capture.
Next comes capture method selection. Post-combustion capture works well for retrofits. Pre-combustion fits integrated systems. Direct air capture makes sense only when point sources aren’t available.
Then comes integration. Capture systems affect heat balance, energy demand, and plant operations. Ignoring this is one of the fastest ways projects fail.
Transport planning follows. Pipelines are efficient but capital-intensive. Shipping offers flexibility. Trucking works only at small scale.
Finally, storage or utilization must be secured before capture begins. Capturing carbon without a destination is like collecting rain without a tank.
Each step matters because each step compounds cost, complexity, and risk if handled poorly.
Tools, Systems, and What Experienced Teams Actually Choose
In practice, most successful projects blend multiple tools rather than relying on a single solution.
Solvent-based capture systems dominate industrial retrofits because they’re proven and scalable. Their downside is energy intensity.
Solid sorbents offer efficiency gains but require precise operating conditions.
Direct air capture tools are improving rapidly but remain expensive and energy-hungry at scale.
Experienced teams prioritize reliability over novelty. The “best” system is the one that runs consistently for decades, not the one with the flashiest pilot results.
Cost curves matter. So does maintenance. So does operator training.
Technology alone never saves a project—systems thinking does.
Common Mistakes That Quietly Kill Carbon Capture Projects
Most failures aren’t technical—they’re strategic.
One common mistake is oversizing systems based on future projections rather than current realities. Another is underestimating energy penalties.
Some teams rush capture without securing long-term storage agreements. Others rely on unproven technologies to meet near-term deadlines.
The most expensive mistake is treating carbon capture technology as a public relations tool instead of an operational system.
When performance matters more than press releases, projects succeed.
The Bigger Picture: What Carbon Capture Technology Can—and Can’t—Do
Carbon capture technology is neither a scam nor a savior.
It won’t replace renewables. It won’t excuse unchecked fossil fuel expansion. And it won’t solve climate change on its own.
What it can do is reduce emissions in places where alternatives are limited, buy time for systemic transitions, and lower cumulative atmospheric carbon.
Used honestly and intelligently, it’s a powerful tool. Used carelessly, it becomes a distraction.
The difference lies in execution.
Conclusion: Moving Forward With Clear Eyes and Practical Intent
Carbon capture technology isn’t about belief—it’s about engineering, economics, and responsibility.
For industries that can’t decarbonize overnight, it offers a realistic path forward. For policymakers, it provides flexibility. For communities, it can mean cleaner air without economic collapse.
The key is discernment.
Understand where it fits. Know its limits. Demand performance, not promises.
If you approach carbon capture technology with clarity rather than ideology, it can be one of the most pragmatic tools available in the fight to reduce emissions—right now, not decades from now.
FAQs
Carbon capture technology is used to capture carbon dioxide emissions from industrial sources or the atmosphere and either store or reuse them to reduce atmospheric CO₂ levels.
Costs vary widely. Point-source capture is significantly cheaper than direct air capture, especially when integrated into existing infrastructure.
Yes, when properly designed and operated. Several large-scale projects have operated successfully for years.
It’s not a replacement. Carbon capture technology complements renewables where emissions are difficult to eliminate.
Yes. CO₂ can be used in fuels, building materials, chemicals, and other industrial products, depending on purity and scale.
TECHNOLOGY
Switching 2nd: The Ultimate Guide to Techniques, Meaning, and Best Practices

If you’ve encountered the term “switching 2nd” and found yourself confused by conflicting definitions, you’re not alone. This phrase represents different concepts across multiple domains, from network engineering to personal productivity. Whether you’re configuring network infrastructure or optimizing your daily workflow, understanding switching 2nd techniques can lead to improved efficiency, better performance, and smoother transitions in your systems and habits.
This comprehensive guide clarifies what switching 2nd really means, explores proven techniques for implementation, and provides actionable best practices you can apply today.
What is Switching 2nd? Definition and Core Concepts
At its core, switching 2nd refers to the strategic implementation or transition to a secondary system, focus, or configuration. The specific meaning depends heavily on context, but the underlying principle remains consistent: creating redundancy, flexibility, or optimized alternatives to enhance overall performance.
The term appears most prominently in two distinct fields, each with its own specialized interpretation and application methods.
Switching 2nd in Computer Networking
In networking environments, switching 2nd typically describes the configuration and deployment of a secondary network switch or the implementation of a second network segment. This approach serves multiple purposes including network redundancy, load balancing, security through network segregation, and failover capabilities.
Common implementations include setting up a backup switch in enterprise environments, configuring VLANs to separate network traffic, creating two bridges for different network purposes, and implementing Layer 2 switching strategies with primary and secondary pathways. Network administrators often use this technique with managed switches, particularly in MikroTik RouterOS environments, to ensure continuous network availability and improved traffic management.
Switching 2nd in Productivity & Personal Development
Beyond the technical realm, switching 2nd represents a cognitive and behavioral strategy for changing your secondary focus, habits, or operational mode. This metaphorical application helps individuals and teams transition smoothly between different priorities, work styles, or attention states.
In this context, the practice involves deliberately shifting your secondary attention or habit patterns, transitioning between complementary productivity systems, and applying cognitive flexibility to enhance task management and personal growth. Rather than abandoning your primary focus, you’re strategically adjusting supporting systems and habits to better align with your goals.
“Switching 2nd” At a Glance: Two Perspectives
| Aspect | Networking Context | Personal Development Context |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Network reliability, security, redundancy | Personal efficiency, adaptability, growth |
| Key Action | Configuring hardware/software infrastructure | Changing habits, focus patterns, routines |
| Tools | Switches, CLI, RouterOS, VLAN configs | Mindfulness apps, planning tools, frameworks |
| Main Benefit | Increased uptime, better traffic management | Reduced stress, improved time management |
| Prerequisites | Networking knowledge, hardware access | Self-awareness, willingness to change |
| Common Challenge | Configuration errors, network loops | Resistance to change, inconsistency |
Why Switching 2nd Matters: Key Benefits and Applications
Understanding and implementing switching 2nd techniques offers tangible advantages regardless of your application domain.
Technical and Operational Benefits
In network environments, switching 2nd provides critical infrastructure improvements. Network redundancy ensures that if your primary switch fails, traffic automatically routes through the secondary system, minimizing downtime. This configuration also enables load balancing, distributing network traffic across multiple paths to prevent bottlenecks and improve overall performance.
Security through separation becomes achievable when you configure distinct network segments for different departments, devices, or security zones. A financial services company might use switching 2nd to isolate their transaction processing network from general office traffic, reducing attack surfaces and improving compliance with regulatory requirements.
Enhanced network management capabilities emerge from this approach as well. Administrators gain greater flexibility to perform maintenance on one switch while the other handles traffic, implement gradual updates without full network outages, and conduct network testing in isolated environments.
Personal and Productivity Benefits
The personal development interpretation of switching 2nd addresses common productivity challenges. By strategically transitioning between complementary work modes or habit patterns, individuals experience reduced cognitive stress from constant context switching and improved adaptability when facing changing priorities or circumstances.
Better time management results from deliberately designing secondary systems that support your primary goals. For example, a software developer might maintain their primary focus on coding while switching their secondary attention pattern from constant email checking to designated communication blocks, preserving deep work periods while remaining responsive.
Personal growth accelerates when you systematically adjust supporting habits and routines. An entrepreneur building a business might switch their secondary fitness routine from sporadic gym visits to brief morning stretching sessions, maintaining health without sacrificing critical business development time.
How to Implement Switching 2nd: Step-by-Step Techniques
Successful implementation requires careful planning and systematic execution, regardless of your application domain.
Pre-Implementation Checklist: Requirements and Planning
Before beginning any switching 2nd initiative, conduct a thorough assessment. Identify your primary objective—what problem are you solving or what improvement are you seeking? Document your current state, whether that’s your existing network topology or your current productivity system and habit patterns.
Determine available resources including hardware, software, time, and budget for technical implementations, or mental energy, tools, and support systems for personal changes. Establish clear success criteria so you can measure whether your switching 2nd implementation achieves its intended results.
Create a rollback plan for technical implementations or an adjustment strategy for personal changes, ensuring you can revert or modify your approach if initial results prove unsatisfactory.
Technique 1: Switching 2nd in a Network (A Practical Guide)
Scenario: Setting Up a Secondary Backup Switch
Consider a small business network currently running on a single managed switch. Implementing switching 2nd creates redundancy and improves reliability.
Step-by-Step Configuration Overview
Begin with network topology planning by mapping your current network, identifying critical devices requiring redundancy, and determining where the secondary switch will physically connect. Ensure compatibility between your primary and secondary switches, ideally using identical models and firmware versions to simplify configuration management.
Configure your secondary switch by accessing its management interface through CLI or GUI, setting a unique management IP address within your network range, and mirroring essential VLAN configurations from your primary switch. Implement Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to prevent network loops, configuring one switch as the root bridge and the other as backup.
Establish physical connections between switches using appropriate trunk ports, verify that STP is blocking the appropriate ports to prevent loops, and configure failover parameters including priority values and convergence timings. Test the failover mechanism by simulating primary switch failure, observing traffic transition to the secondary path, and measuring downtime duration during the switchover.
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting
Broadcast storms from misconfigured STP settings represent the most frequent issue in switching 2nd implementations. Always verify STP configuration before enabling all connections between switches, and monitor for unusual traffic patterns during initial deployment.
IP address conflicts occur when both switches receive identical management IPs or when DHCP scopes overlap across network segments. Maintain detailed documentation of all IP assignments and use distinct subnets for management traffic when possible.
Configuration drift happens over time as changes to the primary switch aren’t replicated to the secondary. Implement regular configuration audits and consider using automated configuration management tools to maintain consistency across your switching infrastructure.
Technique 2: Switching 2nd for Personal Productivity
The “Habit Stacking” Method
Habit stacking provides a structured approach to switching your secondary habits without disrupting primary activities. This technique involves identifying an existing strong habit (your “first” habit), then attaching a new complementary habit (your “second”) immediately before or after it.
Implementation begins with listing your current reliable habits such as morning coffee, lunch break, or evening shutdown routine. Select a secondary habit you want to establish like brief planning, learning activity, or physical movement. Create a specific trigger by linking the new habit to the existing one with a clear statement such as “After I pour my morning coffee, I will review my top three priorities for the day.”
Start with minimal commitment, perhaps just 60 seconds for the new secondary habit, then gradually extend duration as the pattern becomes automatic. This approach leverages existing neural pathways rather than requiring pure willpower to maintain the new behavior.
The “Focus Block” Transition Technique
This method addresses the challenge of switching between different types of work or attention modes throughout your day. Rather than haphazard context switching, you deliberately transition your secondary attention pattern between complementary focus states.
Create distinct work blocks for different types of activities such as deep creative work, collaborative communication, or administrative tasks. Design transition rituals to shift between these blocks, which might include a brief walk, specific music playlist change, or physical location change. Use these rituals to consciously shift your secondary attention pattern from one mode to another.
For example, a consultant might structure their day with morning strategic work (primary focus: client strategy, secondary focus: silence notifications), followed by a transition ritual of brewing tea, then afternoon client communications (primary focus: responsive engagement, secondary focus: time-boxing responses). The transition ritual signals the shift in both primary work type and secondary attention management approach.
Tools and Apps to Facilitate the Switch
Digital tools can support switching 2nd in personal productivity. Time-blocking applications like Timeular or Sunsama help you define and transition between focus blocks with visual cues and reminders. Habit tracking tools such as Habitica or Streaks make secondary habit changes visible and rewarding.
Environment management tools including Forest for focus periods or Brain.fm for attention state optimization provide external support for internal transitions. The key is selecting tools that reduce rather than increase cognitive load during your switching 2nd implementation.
Switching 2nd Best Practices for Success
Regardless of application domain, certain principles enhance switching 2nd effectiveness.
Start small and scale gradually. In networking, begin with non-critical network segments before implementing switching 2nd for mission-critical infrastructure. For personal productivity, establish one secondary habit change before attempting multiple simultaneous transitions.
Document everything meticulously. Network configurations require detailed documentation of switch settings, IP schemes, VLAN assignments, and STP configurations. Personal productivity implementations benefit from journaling about what triggers successful transitions and what obstacles emerge.
Test thoroughly before full deployment. Network changes should be validated in lab environments or during low-traffic periods with comprehensive failover testing. Personal habit changes deserve trial periods where you assess impact before committing fully.
Build in monitoring and feedback loops. Technical implementations need network monitoring tools to track switch performance, failover events, and traffic patterns. Personal implementations require regular reflection to assess whether secondary changes support or hinder primary goals.
Maintain consistency across parallel systems. When running dual network switches, configuration consistency prevents unexpected behavior during failovers. When managing dual productivity modes, consistent transition rituals prevent decision fatigue.
Avoid these common mistakes:
- Implementing switching 2nd without clear objectives or success criteria
- Neglecting to plan for failure scenarios or rollback procedures
- Over-complicating initial implementations with excessive features
- Failing to account for the learning curve during transition periods
- Ignoring feedback indicating that the approach needs adjustment
FAQs
The primary purpose varies by context. In networking, switching 2nd creates redundancy and improves reliability by providing alternative traffic paths and backup infrastructure. In personal productivity, it enables strategic adjustment of secondary focus patterns and supporting habits to better align with primary goals while reducing stress and improving efficiency.
In networking contexts, switching 2nd can include backup switch configuration but encompasses broader concepts like network segmentation and deliberate secondary path creation. The term represents the strategic approach rather than just the hardware redundancy aspect.
Begin with clear goal definition, thorough assessment of your current state, and honest evaluation of available resources. For technical implementations, verify you have necessary hardware access, networking knowledge, and testing capabilities. For personal implementations, ensure you have self-awareness about current patterns, willingness to experiment, and realistic expectations about adjustment periods.
Yes, particularly in personal productivity applications. By deliberately designing how you transition between work modes and adjust secondary attention patterns, you reduce the cognitive burden of constant reactive context switching. This planned approach to transitions helps maintain focus while remaining adaptable to changing circumstances.
Network loops from improper STP configuration, IP address conflicts, configuration inconsistencies between primary and secondary switches, and inadequate failover testing represent the most frequent challenges. Additionally, organizations often underestimate the complexity of maintaining two synchronized network paths over time.
Regular task switching often involves reactive, unplanned shifts between different activities, which creates cognitive overhead and reduces efficiency. Switching 2nd represents a deliberate, strategic approach to adjusting your secondary systems, habits, or infrastructure while maintaining your primary focus or operations. It’s planned transition rather than reactive interruption.
Conclusion
Mastering switching 2nd techniques offers significant advantages whether you’re managing network infrastructure or optimizing personal productivity. By understanding the dual nature of this concept and applying the appropriate techniques for your context, you can achieve greater reliability, improved efficiency, and smoother transitions in your professional and personal systems.
The key to success lies in starting with clear objectives, implementing systematically, and maintaining consistency while remaining open to adjustments based on real-world feedback. Whether you’re configuring redundant network switches or redesigning your daily habits, the principles of thoughtful planning, thorough testing, and continuous monitoring will serve you well.
Begin with one switching 2nd implementation today—choose either a technical or personal application that addresses your most pressing challenge, and apply the techniques outlined in this guide. Your future self, equipped with more resilient systems and optimized workflows, will appreciate the investment.
-

 BLOG7 months ago
BLOG7 months agoDiscovering The Calamariere: A Hidden Gem Of Coastal Cuisine
-

 TECHNOLOGY4 months ago
TECHNOLOGY4 months agoAVtub: The Rise of Avatar-Driven Content in the Digital Age
-

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoChildren’s Flonase Sensimist Allergy Relief: Review
-

 BLOG8 months ago
BLOG8 months agoWarmables Keep Your Lunch Warm ~ Lunch Box Kit Review {Back To School Guide}
-

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoTurkey Neck Fixes That Don’t Need Surgery
-

 TECHNOLOGY7 months ago
TECHNOLOGY7 months agoHow to Build a Mobile App with Garage2Global: From Idea to Launch in 2025
-
 EDUCATION4 months ago
EDUCATION4 months agoHCOOCH CH2 H2O: Structure, Properties, Applications, and Safety of Hydroxyethyl Formate
-

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoMasago: The Tiny Sushi Topping with Big Health Benefits
