TECHNOLOGY
Defined Technology: The Complete Practical Guide to How Modern Systems Are Built, Managed, and Scaled

If you’ve worked in tech long enough—whether as a founder, IT manager, product lead, or even a power user—you’ve probably felt this frustration: technology keeps getting more powerful, but also harder to control.
Servers multiply. Software stacks sprawl. Tools overlap. Costs creep up quietly. And suddenly, no one can clearly explain why a system works the way it does—or how to change it without breaking everything.
That frustration is exactly why defined technology has become such a critical concept.
Defined technology isn’t a buzzword cooked up by vendors. It’s a response to years of reactive, hardware-locked, manually managed systems that simply don’t scale with modern demands. It represents a shift in how technology is designed, governed, and evolved—away from rigid physical constraints and toward logic, abstraction, and intent.
This article is for:
- Business leaders trying to future-proof operations
- IT and engineering teams overwhelmed by system complexity
- Product builders who want flexibility without chaos
- Anyone tired of “it works, but don’t touch it” technology
By the end, you’ll understand what defined technology really means, how it works in practice, where it delivers real value, and how to apply it intelligently—without falling for hype or overengineering.
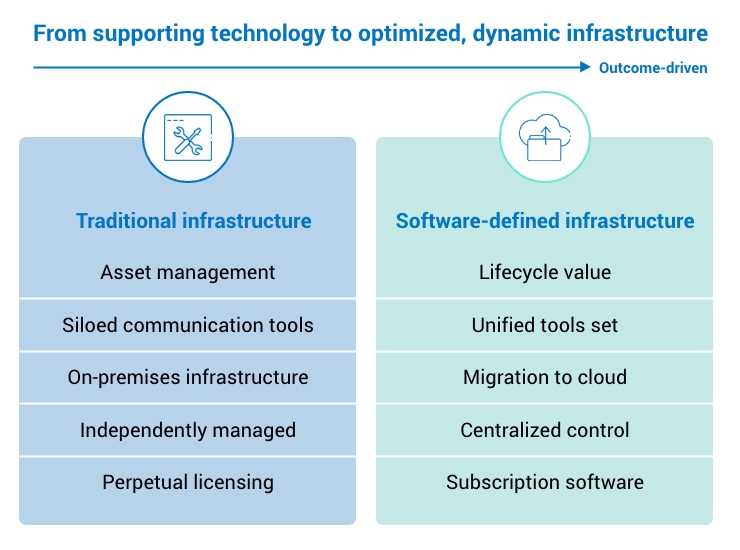
What Is Defined Technology? (From Simple Idea to Expert Understanding)
At its core, defined technology refers to systems where behavior is controlled by software definitions rather than fixed physical components.
Instead of saying:
“This hardware does this one job in this one way”
Defined technology says:
“This system behaves according to rules, policies, and logic we define—and can change when we need it to.”
A Simple Analogy
Think of traditional technology like a mechanical watch. Beautiful, precise—but if you want it to show a second time zone, you need a new watch.
Defined technology is like a smartwatch. The hardware stays the same, but its behavior changes based on software, settings, and user intent.
The power isn’t just flexibility—it’s control at scale.
What Makes Technology “Defined”?
A system qualifies as defined technology when it has these characteristics:
- Abstraction: Physical components are separated from logical control
- Programmability: Behavior can be changed through code or configuration
- Policy-driven control: Rules define outcomes automatically
- Centralized management: Systems are orchestrated, not babysat
- Scalability by design: Growth doesn’t require linear effort
This approach underpins concepts like:
- Software-defined infrastructure
- Infrastructure as code
- Policy-based security
- Cloud-native systems
But defined technology is broader than any single tool or platform—it’s a design philosophy.
Why Defined Technology Matters Right Now (Not Five Years Ago)
A decade ago, systems were smaller, slower, and more predictable. You could afford manual processes and rigid setups.
That world is gone.
Modern systems must handle:
- Rapid scaling (sometimes overnight)
- Remote and distributed teams
- Continuous deployment cycles
- Security threats that evolve daily
- Cost optimization under tight margins
Defined technology thrives in this environment because it assumes change is constant.
Instead of reacting to problems after they happen, defined systems are built to adapt automatically.
This is why industries like finance, healthcare, SaaS, logistics, and even manufacturing are aggressively shifting toward defined models.
Benefits of Defined Technology in Real-World Scenarios

Before Defined Technology
- Configuration done manually
- Changes require downtime
- Scaling means buying hardware
- Knowledge trapped in individuals
- Errors are common and costly
After Defined Technology
- Systems configured once, reused everywhere
- Changes applied consistently and instantly
- Scaling happens through definitions, not purchases
- Knowledge stored in code and policies
- Errors reduced through automation
Who Benefits the Most?
- Startups needing rapid iteration without chaos
- Enterprises managing massive, distributed systems
- IT teams under pressure to do more with less
- Security teams enforcing consistent policies
- Product teams shipping faster with confidence
In practice, defined technology delivers:
- Faster deployment cycles
- Lower operational costs
- Stronger security postures
- Easier audits and compliance
- Better alignment between business intent and technical behavior
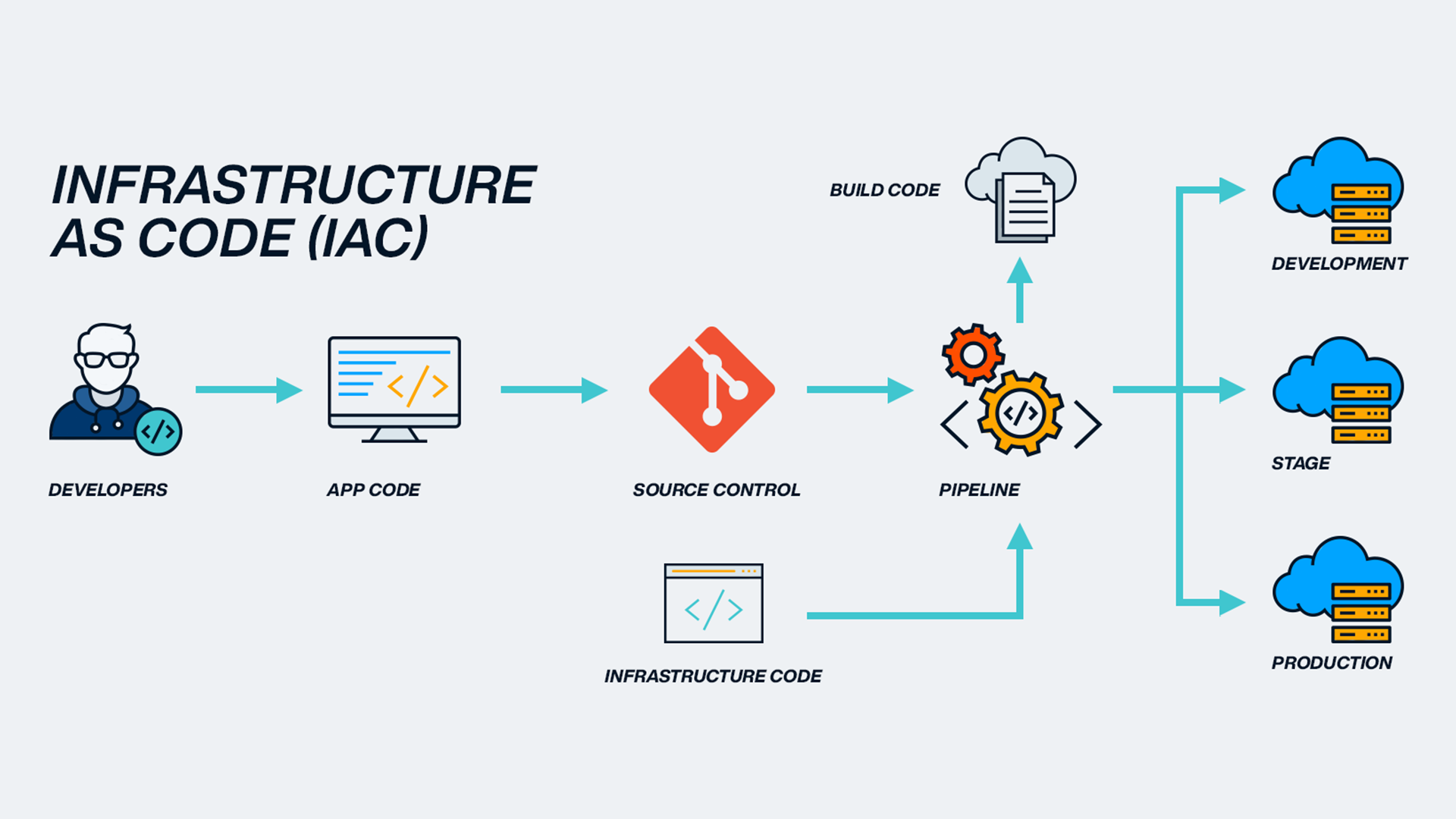
How Defined Technology Works Step by Step
This is where many articles stop being useful. Let’s break it down practically, without theory overload.
Step 1: Separate Logic From Hardware
The first move is abstraction.
Instead of configuring individual machines, you define:
- Desired state
- Performance rules
- Access policies
- Scaling behavior
The hardware becomes interchangeable. The definition becomes the source of truth.
Step 2: Express Intent in Code or Configuration
This is often called declarative control.
You don’t say how to do something step by step.
You say what the outcome should be.
For example:
- “All customer data must be encrypted”
- “Scale this service when traffic exceeds X”
- “Only these roles can access this resource”
The system handles execution.
Step 3: Automate Enforcement
Defined technology shines because it enforces rules automatically.
If something drifts:
- The system corrects it
- Or alerts you
- Or blocks the change
This eliminates configuration drift—one of the biggest hidden risks in traditional systems.
Step 4: Monitor, Adjust, Repeat
Because everything is defined:
- Changes are reversible
- Experiments are safer
- Rollbacks are faster
Over time, systems improve instead of decaying.
Tools and Platforms That Power Defined Technology (What Actually Works)


Free and Beginner-Friendly Options
- Open-source infrastructure-as-code tools
- Policy engines with community support
- Cloud-native configuration services
Best for:
- Learning
- Small teams
- Proof-of-concepts
Limitations:
- Steeper learning curve
- Less enterprise support
Professional and Enterprise-Grade Tools
- Full-stack defined infrastructure platforms
- Advanced orchestration and policy engines
- Integrated security and compliance layers
Best for:
- Regulated industries
- Large-scale systems
- Mission-critical workloads
Trade-offs:
- Cost
- Vendor lock-in if poorly chosen
Expert Recommendation
Start small and intentional.
Defined technology fails when teams try to define everything at once. The smartest teams:
- Define the most painful processes first
- Build confidence
- Expand gradually
Common Mistakes With Defined Technology (And How to Avoid Them)
Mistake 1: Treating It Like a Tool, Not a Philosophy
Buying software doesn’t make your system “defined.”
Fix:
- Redesign workflows
- Document intent
- Train teams to think declaratively
Mistake 2: Over-Automation Too Early
Automation amplifies both good and bad decisions.
Fix:
- Stabilize processes first
- Automate after understanding failure modes
Mistake 3: Ignoring Human Factors
Defined systems still need humans who understand them.
Fix:
- Clear documentation
- Shared ownership
- Simple, readable definitions
Mistake 4: Chasing Trends Instead of Outcomes
Not every system needs full abstraction.
Fix:
- Tie definitions to business goals
- Measure results, not adoption
The Future of Defined Technology (Where This Is Headed)
Defined technology is evolving alongside:
- AI-driven automation
- Predictive infrastructure
- Self-healing systems
- Intent-based networking
The next phase isn’t just defined systems—it’s systems that understand and optimize your intent automatically.
That’s not science fiction. It’s already happening in high-performance environments.
Conclusion: Defined Technology Is About Control, Not Complexity
Defined technology isn’t about replacing humans or adding layers of abstraction for fun.
It’s about:
- Making systems understandable
- Making change safe
- Making growth sustainable
If you’re serious about building technology that lasts—technology that adapts instead of collapses under its own weight—defined technology isn’t optional anymore.
It’s the foundation.
FAQs
Defined technology means systems are controlled by software rules and policies instead of fixed hardware behavior.
No. Small teams often benefit even more because automation reduces manual overhead.
Automation executes tasks. Defined technology controls system behavior and intent at a higher level.
Yes—when implemented correctly, it enforces consistent policies and reduces human error.
Cloud uses defined technology principles, but defined technology can exist outside the cloud.
TECHNOLOGY
3dm ai: The Practical, Real-World Guide to AI-Powered 3D Modeling That Actually Delivers Results

If you’ve ever stared at a blank 3D viewport at 2 a.m., wondering why a “simple” model is eating your entire week, you already understand the pain that 3dm ai is trying to solve.
For years, 3D creation has lived at an uncomfortable intersection:
incredible creative freedom on one side, brutally steep learning curves and time costs on the other. Whether you’re a game developer racing a deadline, a product designer iterating prototypes, or a marketer who just needs decent 3D visuals without hiring an entire studio, the friction has always been real.
That’s where 3dm ai enters the conversation—not as hype, not as magic, but as a shift in how 3D work gets done.
This guide is written for:
- Creators who already understand how painful traditional 3D workflows can be
- Beginners who want to enter 3D without drowning in complexity
- Professionals who care about speed, iteration, and output quality
- Decision-makers evaluating whether AI-powered 3D tools are actually worth adopting
By the end, you’ll understand what 3dm ai really is, how it works in practice, where it shines, where it fails, and how to use it intelligently without compromising quality or credibility.
What is 3dm ai? A clear explanation from beginner to expert
At its core, 3dm ai refers to the use of artificial intelligence to generate, modify, optimize, or assist with 3D models, textures, materials, and scenes. Instead of manually sculpting every vertex or painstakingly unwrapping UVs, AI systems learn patterns from massive datasets of existing 3D assets and apply that knowledge to accelerate creation.
A helpful analogy:
Traditional 3D modeling is like carving a statue from stone.
3dm ai is like starting with a rough, intelligent clay form that already understands anatomy, proportion, and structure—and then refining it.
At the beginner level, 3dm ai often looks like:
- Text-to-3D generation (“Create a medieval sword with worn metal”)
- Image-to-3D conversion from photos or sketches
- Automatic retopology and mesh cleanup
At the advanced level, it becomes:
- AI-assisted procedural modeling
- Smart material generation and texture synthesis
- LOD creation and asset optimization for real-time engines
- Batch generation of asset variations for large-scale projects
What matters is not that AI replaces artists—it doesn’t—but that it removes the slow, repetitive, error-prone parts of the pipeline so human creativity can focus on decisions, style, and storytelling.
Why 3dm ai is taking off now (and not five years ago)
The idea of AI in 3D isn’t new. What is new is that several bottlenecks have finally broken at once.
First, training data. High-quality 3D datasets are now large enough to train usable models. Second, compute power. GPUs and cloud infrastructure can finally handle the complexity of 3D geometry at scale. Third, demand. Real-time 3D is everywhere—from games and AR to e-commerce and virtual production.
But the biggest driver is economic pressure.
Studios are being asked to produce:
- More assets
- At higher quality
- Across more platforms
- In less time
3dm ai doesn’t eliminate skill—it amplifies it. The best results come from people who understand both 3D fundamentals and AI-assisted workflows.
Real benefits and use cases: where 3dm ai actually works
This is where theory meets reality.
Game development
In game pipelines, asset volume is the silent killer. A single environment can require hundreds or thousands of models.
3dm ai helps by:
- Generating base meshes for props and environments
- Creating multiple visual variations from one prompt
- Auto-optimizing topology for real-time engines
Developers still polish assets in tools like Unity or Unreal Engine, but AI drastically reduces the initial modeling time.
Product design and prototyping
For industrial and product designers, speed matters more than perfection early on.
With 3dm ai:
- Concept models can be generated in minutes
- Iterations become cheaper and faster
- Stakeholders can visualize ideas before CAD-level precision
The “before vs after” difference is dramatic: days of modeling become hours of refinement.
Marketing and e-commerce
Brands increasingly rely on 3D visuals for ads, product pages, and AR previews.
3dm ai allows teams to:
- Generate photorealistic product models without full scans
- Create scene variations for campaigns
- Adapt assets across platforms quickly
For marketing teams without deep 3D expertise, this is often the first viable entry point.
Architecture and visualization
While still imperfect, AI-assisted 3D is being used to:
- Block out buildings and interiors
- Generate furniture and environmental assets
- Speed up early-stage visualization
Final renders still require human control, but early ideation is faster and cheaper.
A step-by-step practical workflow using 3dm ai
This is where most guides fall apart, so let’s keep it grounded.
Step 1: Define intent before touching AI
The biggest mistake people make is asking AI to “just make something cool.”
Instead, define:
- Asset type (prop, character, environment)
- Target platform (game, render, web, AR)
- Quality level (concept, mid-poly, production-ready)
AI works best when constraints are clear.
Step 2: Generate a base model, not a final asset
Use 3dm ai tools to create:
- A rough but proportionally correct mesh
- Initial material and texture suggestions
Treat this as a starting point, not a deliverable.
Step 3: Manual cleanup and refinement
This is where real expertise matters.
Most AI-generated models need:
- Topology cleanup
- UV fixes
- Scale and proportion adjustments
Tools like Blender remain essential here.
Step 4: Optimization for the target platform
AI can assist with:
- Automatic LOD generation
- Polygon reduction
- Texture baking
But always test assets in-engine or in your rendering environment.
Step 5: Artistic polish and validation
Final touches—edge wear, stylization, storytelling—are human-driven. This is where AI stops and craft begins.
Tools, comparisons, and honest recommendations
Not all 3dm ai tools are created equal.
Free and beginner-friendly tools
Pros:
- Easy to experiment
- Low barrier to entry
Cons:
- Limited control
- Inconsistent output quality
Best for learning and rapid ideation.
Professional and paid solutions
Pros:
- Better topology and texture results
- Integration with existing pipelines
Cons:
- Cost
- Requires 3D fundamentals to use effectively
Best for studios and serious creators.
Hybrid workflows (the sweet spot)
In practice, most professionals use:
- AI for generation and acceleration
- Traditional tools for refinement and control
This balance delivers speed without sacrificing quality.
Common mistakes with 3dm ai (and how to avoid them)
Treating AI output as “done”
AI models almost always need cleanup. Skipping this step leads to broken assets and technical debt.
Ignoring topology fundamentals
Bad topology causes animation issues, shading artifacts, and performance problems—AI doesn’t magically solve this.
Over-relying on prompts
The best results come from iteration, not clever wording.
Forgetting legal and licensing concerns
Always understand how AI-generated assets can be used commercially.
Where 3dm ai is heading next
Based on current trajectories, expect:
- Better semantic understanding of prompts
- Improved animation-ready topology
- Deeper integration into mainstream 3D software
- AI-assisted rigging and animation
But even as tools improve, the core truth remains:
AI accelerates skill—it doesn’t replace it.
Conclusion: using 3dm ai intelligently, not blindly
3dm ai is not a shortcut to mastery, and it’s not a threat to real creators. It’s a lever—one that multiplies output when used with intention and experience.
If you approach it with clear goals, strong fundamentals, and realistic expectations, it can:
- Save enormous amounts of time
- Lower creative barriers
- Expand what small teams and individuals can achieve
The creators who win won’t be the ones who resist AI or blindly trust it—they’ll be the ones who learn how to work with it.
FAQs
Typically base meshes, textures, materials, and variations—not final, production-ready assets.
Yes, but learning basic 3D concepts dramatically improves results.
No. It replaces repetitive tasks, not creative judgment.
Yes, especially for prototyping and environment props.
Almost always—manual refinement is essential.
TECHNOLOGY
AC AI: The Complete Expert Guide to AI-Powered Air Conditioning (From First-Time Buyers to Industry Pros)

Have you ever noticed how your air conditioner never quite gets it right?
Some days it overcools the room until you’re reaching for a blanket. Other days it runs nonstop, drives up your electricity bill, and still leaves the space feeling uneven and uncomfortable. For years, we accepted this as “just how AC works.”
That assumption is finally breaking.
AC AI is redefining what air conditioning means in homes, offices, factories, hospitals, and smart cities. Instead of blindly following temperature settings, AI-powered air conditioning systems learn from your behavior, adapt to your environment, and optimize themselves in real time. They don’t just cool air — they make intelligent decisions.
This guide is written for homeowners, facility managers, HVAC professionals, smart-home enthusiasts, and business owners who want to understand AC AI beyond marketing buzzwords. You’ll learn what AC AI really is, how it works in the real world, where it delivers measurable value, and how to choose the right tools without wasting money.
If you’ve ever wondered whether AI in air conditioning is worth it — or inevitable — this article will give you clarity, confidence, and practical next steps.
What Is AC AI? A Beginner-Friendly Explanation That Scales to Expert Level
At its core, AC AI refers to the use of artificial intelligence technologies — such as machine learning, sensors, predictive analytics, and automation — to control, optimize, and improve air conditioning systems.
Traditional AC systems are reactive. You set a temperature, and the system turns on or off based on basic thresholds. AC AI systems are proactive. They observe patterns, predict needs, and make adjustments before discomfort or inefficiency happens.
Think of it like the difference between a manual car and a self-driving one. A traditional AC is like pressing the accelerator and brake yourself every few seconds. AC AI is like cruise control that adapts to traffic, hills, and driving habits automatically.
How AC AI Actually Works Behind the Scenes
An AI-enabled AC system typically combines several layers:
Sensors continuously collect data such as room temperature, humidity, occupancy, outdoor weather, sunlight exposure, and even air quality.
Machine learning models analyze historical and real-time data to understand patterns — when people are home, which rooms heat up fastest, how weather affects cooling demand.
Decision engines adjust compressor speed, airflow, cooling cycles, and schedules dynamically rather than using fixed rules.
Feedback loops allow the system to learn from outcomes. If users override settings, the AI adapts future behavior accordingly.
Over time, the system becomes more accurate, more efficient, and more personalized.
AC AI Is Not Just “Smart Thermostats”
A common misconception is that AC AI equals a smart thermostat. While smart thermostats are part of the ecosystem, AC AI goes much deeper. It can control multi-zone systems, predict maintenance failures, balance energy loads across buildings, and integrate with solar power or smart grids.
In large facilities, AC AI can coordinate hundreds of units simultaneously. In homes, it can learn individual comfort preferences room by room.
This scalability is why AC AI matters not just for convenience, but for energy sustainability at a global level.
Why AC AI Matters Right Now (And Not Five Years Ago)
The rise of AC AI isn’t accidental. Several real-world pressures are converging at the same time.
Electricity costs are rising worldwide, making inefficient cooling systems financially painful. Climate change is increasing cooling demand, especially in already hot regions. Buildings account for a massive share of global energy consumption, and HVAC is the largest contributor within buildings.
At the same time, AI technology has matured. Sensors are cheaper. Cloud computing is accessible. Edge AI allows real-time decisions without constant internet dependency.
In short, AC AI is no longer experimental. It’s practical, proven, and increasingly expected.
Benefits of AC AI and Real-World Use Cases That Actually Deliver Results



Who Benefits the Most From AC AI?
AC AI isn’t limited to tech enthusiasts or luxury homes. Its value spans multiple audiences.
Homeowners benefit from lower electricity bills, better sleep quality, and reduced manual adjustments.
Businesses benefit from predictable energy costs, improved employee comfort, and fewer system breakdowns.
Hospitals and labs benefit from precise climate control that protects patients, equipment, and sensitive materials.
Industrial facilities benefit from load optimization, compliance, and predictive maintenance.
Before vs After: The Practical Impact
Before AC AI, cooling systems ran on fixed schedules. Offices cooled empty rooms at night. Homes wasted energy while residents were away. Maintenance was reactive — something broke, then it got fixed.
After AC AI, systems respond to actual occupancy. Cooling intensity adapts to real needs. Energy usage flattens instead of spiking. Maintenance issues are detected before failure.
These aren’t abstract benefits. Real-world deployments consistently show energy savings between 15% and 40%, depending on scale and configuration.
Industry-Specific Scenarios
In smart homes, AC AI integrates with voice assistants, window sensors, and sleep schedules to create personalized comfort.
In hotels, AI adjusts room temperatures based on check-in status, reducing waste without affecting guest experience.
In data centers, AI balances cooling loads dynamically, preventing hotspots while minimizing power draw.
In retail, AC AI optimizes comfort during peak hours while reducing costs during low foot traffic.
This adaptability is what makes AC AI fundamentally different from previous “efficient” systems.
Step-by-Step Practical Guide: How to Implement AC AI the Right Way
Implementing AC AI isn’t about buying the most expensive system. It’s about making smart, staged decisions.
Step 1: Understand Your Current Cooling Pain Points
Start by identifying what’s actually broken.
Are energy bills unpredictable?
Do some rooms feel uncomfortable no matter the setting?
Is maintenance reactive and costly?
Do users constantly override settings?
AC AI works best when it solves real problems, not imagined ones.
Step 2: Decide Between Retrofit vs AI-Native Systems
Retrofit solutions add AI control layers to existing AC systems. They’re cost-effective and ideal for most homes and small businesses.
AI-native systems are built with intelligence at the hardware level. They’re powerful but typically suited for new construction or large facilities.
There’s no universal right answer — only what fits your context and budget.
Step 3: Choose the Right Level of Intelligence
Not everyone needs full automation. Some users prefer AI suggestions with manual control. Others want fully autonomous operation.
The key is choosing a system that allows gradual trust-building rather than forcing automation immediately.
Step 4: Integrate With Broader Systems
AC AI works best when connected to weather data, occupancy sensors, smart meters, or solar systems. Integration multiplies value.
Step 5: Monitor, Learn, and Fine-Tune
The first few weeks are a learning phase. Let the system observe patterns. Provide feedback. Fine-tune comfort ranges.
The biggest mistake is disabling AI too early before it finishes learning.
AC AI Tools, Platforms, and Expert Recommendations


Consumer-Level Solutions
Products from companies like Daikin, LG, and Samsung increasingly embed AI into residential AC units.
Pros:
Easy installation
Integrated hardware and software
Strong brand support
Cons:
Limited customization
Vendor lock-in
Smart Thermostat Ecosystems
Platforms such as Google Nest and Ecobee focus on AI-driven control layered over existing systems.
Pros:
Affordable entry point
Strong learning algorithms
Good app experience
Cons:
Dependent on compatibility
Less control over mechanical behavior
Enterprise and Commercial AI HVAC Platforms
Solutions from Honeywell and Johnson Controls provide advanced analytics, predictive maintenance, and multi-building optimization.
Pros:
Deep insights
Scalable across facilities
Proven ROI
Cons:
Higher cost
Longer implementation cycles
Expert Recommendation
For homes and small offices, start with AI-enabled thermostats or retrofit controllers. For large buildings, invest in centralized AI platforms with professional commissioning.
The best system is the one people actually use and trust.
Common AC AI Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
Mistake 1: Expecting Instant Perfection
AI needs data. Expecting perfect comfort in the first week leads to disappointment. Give it time to learn.
Fix: Allow a learning period and resist constant manual overrides.
Mistake 2: Over-Automating Too Quickly
Full autonomy without user trust leads to frustration.
Fix: Start with assisted automation, then scale up.
Mistake 3: Ignoring Sensor Placement
Poor sensor placement leads to bad decisions.
Fix: Ensure sensors reflect real living or working conditions.
Mistake 4: Chasing Features Over Outcomes
More features don’t mean better results.
Fix: Focus on energy savings, comfort stability, and reliability.
What Most People Miss
AC AI is not set-and-forget. It’s a partnership between human preferences and machine learning.
The Future of AC AI: Where This Is All Headed
AC AI is moving toward self-healing systems that detect faults before humans notice. Integration with smart grids will allow systems to cool more when electricity is cheaper or greener.
In the long run, AC AI won’t be a feature — it will be the default expectation.
Conclusion: Why AC AI Is Worth Understanding and Adopting Now
AC AI isn’t hype. It’s a response to real energy, comfort, and sustainability challenges. When implemented thoughtfully, it saves money, improves daily life, and reduces environmental impact.
Whether you’re upgrading a home unit or managing a commercial facility, understanding AC AI gives you leverage. It turns cooling from a cost center into a strategic advantage.
The smartest move isn’t rushing in — it’s starting informed.
FAQs
AC AI means using artificial intelligence to automatically control and optimize air conditioning based on real-world conditions and behavior.
Costs vary, but many solutions pay for themselves through energy savings.
Yes, many retrofit solutions are designed specifically for older systems.
In most cases, yes — especially where usage patterns are inconsistent.
Modern systems are designed with fail-safes and manual overrides.
TECHNOLOGY
IA AI: The Practical, Real-World Guide to Intelligent Automation That Actually Works

If you’ve spent any time around technology conversations lately, you’ve probably heard the phrase IA AI thrown around with equal parts excitement and confusion. Some people talk about it like it’s magic. Others treat it like an abstract buzzword that belongs only in research labs or Silicon Valley boardrooms.
Here’s the truth I’ve learned from years of working with automation tools, analytics platforms, and AI-driven systems across content, operations, and growth teams: IA AI is neither hype nor magic—it’s leverage. And like any powerful lever, it only works when you understand where to place it and how much pressure to apply.
This guide is written for founders, marketers, operators, developers, creators, and decision-makers who don’t want vague theory. It’s for people who want to understand what IA AI actually is, how it works in the real world, where it delivers measurable ROI, and how to implement it without burning time, money, or credibility.
By the time you finish this article, you’ll understand IA AI at a beginner-friendly level and have the depth to speak about it confidently with engineers, stakeholders, or clients. More importantly, you’ll know how to use it.
IA AI Explained Clearly: From Simple Concept to Advanced Understanding
At its core, IA AI refers to Intelligent Automation powered by Artificial Intelligence. It’s the fusion of traditional automation (rule-based systems that follow instructions) with adaptive AI models that learn, predict, and improve over time.
A helpful way to think about it is this:
Traditional automation is like a conveyor belt.
IA AI is like a skilled worker who watches the belt, notices problems, adjusts the process, and improves efficiency every day.
Automation alone follows rules. AI alone analyzes data. IA AI combines both—execution plus intelligence.
In practical terms, IA AI systems can:
- Understand unstructured data like text, images, audio, and video
- Make decisions based on probability, not just rules
- Learn from outcomes and improve performance
- Scale processes that previously required human judgment
This is why IA AI feels different from older software. It doesn’t just do tasks faster—it does smarter work.
Behind the scenes, IA AI typically blends several technologies:
- Machine learning models for pattern recognition
- Natural language processing for understanding human input
- Predictive analytics for forecasting outcomes
- Workflow automation engines for execution
Platforms like OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft have accelerated this shift by making advanced AI accessible through APIs and tools instead of PhD-only research.
The result? IA AI has moved from experimental to operational—and that changes everything.
Why IA AI Matters Right Now (And Why Timing Is Critical)
There’s a reason IA AI feels unavoidable in 2026: the economics have flipped.
Five years ago, intelligent automation required:
- Custom models
- Expensive infrastructure
- Long deployment cycles
- Specialized teams
Today, cloud-based AI, pre-trained models, and no-code automation tools mean IA AI is faster, cheaper, and more reliable than ever.
From a business perspective, three pressures are colliding:
- Rising labor costs
- Exploding data volumes
- Customer expectations for speed and personalization
IA AI sits at the intersection of all three. It allows organizations to scale output without scaling headcount, make sense of massive datasets, and deliver personalized experiences at machine speed.
From personal experience, the biggest shift isn’t productivity—it’s decision quality. IA AI systems don’t get tired, emotional, or distracted. They surface patterns humans miss and handle repetitive decisions with ruthless consistency.
That’s why companies adopting IA AI early aren’t just more efficient—they’re more resilient.
Real Benefits of IA AI You Can Measure (Not Just Talk About)
The real value of IA AI shows up in outcomes, not demos.
Time Compression
Processes that once took days—reporting, analysis, approvals—now happen in minutes. IA AI removes friction between data, decision, and action.
Cost Reduction Without Quality Loss
Unlike outsourcing or aggressive automation, IA AI often improves quality while lowering costs. Fewer errors, faster responses, better predictions.
Human Focus Shift
One of the most underrated benefits: IA AI pushes humans toward higher-value work. Strategy, creativity, judgment, and relationships become the focus again.
Scalable Personalization
From marketing emails to customer support responses, IA AI enables one-to-one personalization at scale—something humans simply can’t do manually.
The before-and-after contrast is stark:
- Before IA AI: reactive, manual, inconsistent
- After IA AI: proactive, adaptive, data-driven
IA AI in the Real World: Where It’s Actually Used Today
IA AI isn’t limited to tech companies. It’s everywhere once you know what to look for.
In marketing, IA AI powers content optimization, predictive audience targeting, and conversion forecasting. Tools connected to platforms like HubSpot and Salesforce automate segmentation and follow-ups that once required entire teams.
In operations, IA AI predicts inventory needs, flags anomalies in supply chains, and optimizes logistics routes.
In finance, it detects fraud patterns, automates reconciliations, and improves forecasting accuracy.
In healthcare, IA AI assists diagnostics, scheduling, and patient triage—augmenting professionals rather than replacing them.
The common thread across industries is decision support at scale.
A Step-by-Step Practical Guide to Implementing IA AI Successfully
This is where most people go wrong—jumping straight to tools without strategy.
Step 1: Identify Decision Bottlenecks
IA AI works best where humans make repetitive decisions with incomplete information. Look for:
- High volume
- Clear success metrics
- Historical data availability
Step 2: Start With Augmentation, Not Replacement
The most successful IA AI projects enhance human workflows first. This builds trust, improves adoption, and surfaces edge cases early.
Step 3: Choose the Right Level of Intelligence
Not every process needs deep learning. Sometimes rule-based automation plus light AI is more reliable and cheaper.
Step 4: Integrate Feedback Loops
IA AI systems improve only when outcomes are measured. Build feedback into every workflow.
Step 5: Scale Gradually
Expand horizontally once one workflow proves ROI. Avoid the temptation to “AI everything” at once.
From experience, this phased approach prevents 80% of IA AI failures.
IA AI Tools: Honest Comparisons and Expert Picks

Not all IA AI tools are created equal.
Beginner-friendly options often focus on no-code automation layered with AI suggestions. They’re fast to deploy but limited in customization.
Professional platforms offer deeper control, better integrations, and stronger data governance—but require expertise.
A practical stack often includes:
- An AI model provider like OpenAI
- An automation layer such as Zapier
- A data platform like Snowflake
The key isn’t brand—it’s fit. The best IA AI tool is the one your team will actually use.
Common IA AI Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
The most damaging mistake is expecting instant intelligence. IA AI improves over time. Early results are directional, not perfect.
Another common failure is poor data hygiene. Garbage data produces confident but wrong AI outputs—arguably worse than no automation at all.
Finally, many teams underestimate change management. IA AI changes how people work, not just what tools they use. Training and communication matter.
The fix is simple but not easy: start small, measure obsessively, and involve users early.
The Future of IA AI: What’s Coming Next
IA AI is moving toward:
- More autonomous decision-making
- Deeper personalization
- Better explainability
- Tighter human-AI collaboration
The organizations that win won’t be the ones with the most AI—they’ll be the ones with the best judgment about where to use it.
Conclusion: Why IA AI Is a Skill, Not Just a Technology
IA AI isn’t something you “install and forget.” It’s a capability you develop.
When used thoughtfully, it becomes a competitive advantage that compounds over time. When used carelessly, it becomes an expensive distraction.
The opportunity right now is enormous. The barrier to entry is lower than ever. And the companies and individuals who learn IA AI deeply—not superficially—will shape how work gets done for the next decade.
If you take one action after reading this, let it be this: identify one decision you make repeatedly and ask how IA AI could make it smarter. That’s where transformation begins.
FAQs
IA AI refers to Intelligent Automation combined with Artificial Intelligence, enabling systems to execute tasks while learning and adapting.
No. Machine learning is a component. IA AI includes automation, workflows, and decision logic on top of AI models.
Absolutely. Cloud-based tools have made IA AI accessible without enterprise budgets.
In practice, it reshapes roles more than replaces them, shifting humans toward higher-value work.
Well-scoped projects often show measurable results within 60–90 days.
-

 HEALTH7 months ago
HEALTH7 months agoChildren’s Flonase Sensimist Allergy Relief: Review
-

 BLOG6 months ago
BLOG6 months agoDiscovering The Calamariere: A Hidden Gem Of Coastal Cuisine
-

 TECHNOLOGY3 months ago
TECHNOLOGY3 months agoAVtub: The Rise of Avatar-Driven Content in the Digital Age
-

 TECHNOLOGY6 months ago
TECHNOLOGY6 months agoHow to Build a Mobile App with Garage2Global: From Idea to Launch in 2025
-

 BLOG7 months ago
BLOG7 months agoWarmables Keep Your Lunch Warm ~ Lunch Box Kit Review {Back To School Guide}
-

 HEALTH7 months ago
HEALTH7 months agoTurkey Neck Fixes That Don’t Need Surgery
-
 EDUCATION3 months ago
EDUCATION3 months agoHCOOCH CH2 H2O: Structure, Properties, Applications, and Safety of Hydroxyethyl Formate
-

 BLOG6 months ago
BLOG6 months agoKeyword Optimization by Garage2Global — The Ultimate 2025 Guide
