TECHNOLOGY
Eco-Friendly Technologies for Sustainable Living: A Complete Guide for a Greener Future

If you’ve ever stood in the grocery aisle comparing “eco-friendly” labels or wondered whether solar panels are worth the investment, you’re not alone. Today, more people want to live sustainably—but the world of green technology can feel confusing, expensive, or even out of reach. The truth? Eco-friendly technologies for sustainable living are more accessible, practical, and impactful than ever before, no matter your lifestyle or budget.
In this guide, you’ll learn what sustainable technologies actually are, how they work in everyday life, and which solutions make the biggest difference for your home, wallet, and the planet. Whether you’re a homeowner, renter, small business owner, or someone simply trying to reduce your carbon footprint, this article will help you understand the options—and start using them with confidence.
What Are Eco-Friendly Technologies for Sustainable Living?
At their core, eco-friendly technologies are tools, systems, and innovations designed to reduce environmental impact, minimize resource consumption, and support long-term ecological balance. Think of them as modern upgrades that help us live smarter: they use less energy, create less waste, and often save money in the process.
An easy analogy is to think of sustainable technology like switching from an old flip phone to a smartphone. You still make calls, but the experience becomes far more efficient, intuitive, and valuable. Eco-friendly tech does the same for everyday living—only instead of boosting productivity, it boosts sustainability.
Examples of Eco-Friendly Technologies You Already Know
- Solar panels powering homes and businesses
- Smart thermostats automatically reducing energy waste
- LED lights that last decades
- Greywater recycling systems
- Composting machines that turn food scraps into usable soil
- Electric vehicles and e-bikes
- Energy-efficient appliances
- Water-saving fixtures
These technologies aren’t futuristic—they’re here, widely available, and increasingly affordable.
Why Eco-Friendly Technologies Matter Today
There’s a reason conversations around sustainability have grown so urgent. Climate change, rising energy costs, water scarcity, and excessive waste affect all of us. Eco-friendly technologies offer a realistic, actionable solution. Here’s why they matter:
1. They Reduce Carbon Footprint
Most homes generate emissions through electricity, heating, appliances, and transportation. Green tech helps lower this impact dramatically.
2. They Cut Long-Term Costs
Energy-efficient devices use fewer resources, leading to lower utility bills. Solar panels, for instance, often pay for themselves within 5–7 years.
3. They Conserve Limited Resources
Water-saving systems, composters, and efficient appliances prevent unnecessary waste.
4. They Improve Quality of Life
Smart energy systems create more comfortable living spaces, cleaner air, and healthier homes.
5. They Future-Proof Your Lifestyle
As governments shift policies toward sustainability, eco-friendly technologies keep individuals and businesses aligned with the future.
Benefits & Use Cases of Eco-Friendly Technologies
Let’s explore how these technologies fit into real, everyday life—no jargon, no unrealistic scenarios.
1. In the Home
Sustainable home technologies are the easiest place to start.
Solar Energy Systems
Solar panels, solar water heaters, and solar batteries help households generate clean electricity while reducing or even eliminating grid dependency. In sunny regions, homeowners can save thousands of dollars over time.
Smart Home Energy Management
Devices like smart thermostats, plugs, energy monitors, and automated lights help reduce waste without sacrificing comfort. These are especially beneficial for busy families.
Eco-Friendly Appliances
Refrigerators, washers, dryers, and dishwashers now use drastically less energy and water than older models. Their impact compounds over years of daily use.
Water Conservation Systems
Low-flow faucets, high-efficiency toilets, and greywater systems cut water use by up to 50%—especially valuable in drought-prone areas.
2. In Transportation
Transportation contributes significantly to carbon emissions. Eco-friendly alternatives include:
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, require less maintenance, and cost less to operate over their lifetime. Even renters can benefit through public charging stations.
E-Bikes and Electric Scooters
Perfect for short commutes or city travel. They reduce road congestion and provide an affordable transportation option.
Carpooling and Ride-Sharing Apps
Not exactly “technology” in the hardware sense, but digitally powered solutions that significantly cut emissions for everyday commuters.
3. In Everyday Lifestyle Choices
Small shifts can make a big impact:
Smart Meters
These track and optimize home electricity use in real time.
Indoor Composters
Electric composters turn kitchen scraps into nutrient-rich soil in hours—ideal for apartments.
Biodegradable Household Products
From packaging to cleaning supplies, biodegradable tech reduces landfill waste.
Sustainable Water Filtration
Advanced filters reduce reliance on plastic bottles while ensuring safe home drinking water.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Adopting Eco-Friendly Technologies
You don’t need to overhaul your home overnight. Here’s a practical roadmap for transitioning into sustainable living technologies—at your own pace.
Step 1: Assess Your Current Environmental Impact
Start by identifying your biggest areas of consumption:
- Electricity usage
- Water consumption
- Transportation habits
- Waste production
- Types of appliances and age of devices
Tools like home energy audits or smart energy monitors can provide clarity.
Tip:
Begin with simple tracking—utility bills, time-of-use patterns, and appliance age.
Step 2: Set Achievable Sustainability Goals
These might include:
- Reducing electricity consumption by 20%
- Cutting water usage by half
- Eliminating single-use plastics
- Switching to green transportation three times a week
- Installing small-scale solar solutions
Goals keep you focused and help prioritize investments.
Step 3: Start with Low-Cost, High-Impact Upgrades
These offer huge value without requiring major renovations:
- Replace bulbs with LEDs
- Install a smart thermostat
- Use power strips to eliminate standby energy drain
- Integrate water-saving showerheads
- Adopt reusable and biodegradable household items
These changes can immediately reduce bills and environmental impact.
Step 4: Move to Intermediate Upgrades
Once the basics are set, consider:
- Energy-efficient appliances
- Smart irrigation systems
- Indoor composters
- Solar phone chargers
- Smart blinds to control heat gain
These bring noticeable improvements and often qualify for rebates.
Step 5: Invest in Long-Term Sustainable Technologies
These require planning but deliver substantial returns:
- Solar panels
- Solar storage batteries
- Electric vehicles
- Greywater recycling systems
- Rainwater harvesting
- Home insulation upgrades
Best Practice:
Check for government incentives, tax credits, and financing programs—they can reduce upfront costs significantly.
Tools, Comparisons & Recommendations
Here’s a practical breakdown of tools that genuinely add value (not just what looks trendy).
Solar Tech Options
1. Rooftop Solar Panels
Pros: Major savings, renewable energy, long lifespan
Cons: Requires roof space; higher upfront cost
Best for: Homeowners with high sunlight exposure
2. Portable Solar Generators
Great for renters or travelers.
3. Solar Water Heaters
More affordable than full panels and reduce water heating bills dramatically.
The Smart Home Devices
Smart Thermostats (e.g., Nest, Ecobee)
- Learn your patterns
- Reduce energy waste
- Offer remote control
Smart Plugs & Power Strips
Perfect for eliminating standby power consumption.
Home Energy Monitors
Sense or Emporia systems give real-time insights into which appliances consume the most power.
Water-Saving Technologies
Greywater Systems
Recycle shower and sink water for irrigation.
Rain Harvesting Kits
Capture rainwater for gardening and outdoor cleaning.
Smart Irrigation
Adjusts watering based on weather and soil conditions.
Transportation Technologies
EVs vs Hybrid Cars
| Feature | EV | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|
| Emissions | Zero tailpipe | Lower than gas |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate |
| Range | Depends on battery | Long |
| Best for | Urban commuting | Mixed driving |
Electric Bikes
Affordable, quick, and efficient—perfect for city dwellers.
Common Mistakes & How to Fix Them
Even well-intentioned sustainable living efforts can go wrong. Here’s what to avoid:
Mistake 1: Trying to Do Everything at Once
This leads to overwhelm or unsustainable spending.
Fix:
Start small. Build momentum. Prioritize changes with the highest impact.
Mistake 2: Buying Tech Without Understanding Usage
A smart device is only smart if you use it effectively.
Fix:
Read usage guides, personalize settings, and utilize automation features.
Mistake 3: Overestimating Solar Savings in Low-Sun Locations
Not all roofs are ideal for solar.
Fix:
Get a professional solar assessment or use tools like Google’s Project Sunroof.
Mistake 4: Ignoring Maintenance
Even sustainable tech needs upkeep.
Fix:
- Clean solar panels
- Replace water filters
- Update smart home software
- Service EV batteries as recommended
Mistake 5: Believing Eco-Friendly Tech Is Always Expensive
Many assume sustainable technology costs a fortune.
Fix:
Leverage rebates, local incentives, and budget-friendly alternatives—like portable solar or smart plugs.
Conclusion: Building a Future That’s Smarter, Cleaner & More Sustainable
Eco-friendly technologies for sustainable living aren’t just about saving the planet—they’re about improving our everyday lives. They help us lower costs, reduce environmental impact, and create homes and communities that support long-term well-being.
The best part? You don’t need to be an engineer or environmental expert to start. Every small step, from switching to LED bulbs to installing solar panels, moves you closer to a greener future.
If you’re ready to take the next step, start exploring one sustainable upgrade this week. Have questions or want personalized recommendations? Drop a comment—I’m here to help guide your journey.
FAQs
LED bulbs, smart plugs, low-flow fixtures, and indoor composters are inexpensive and deliver immediate results.
Yes—especially in sunny regions. They reduce utility bills, increase home value, and often pay for themselves within a few years.
Absolutely. Renters can use portable solar chargers, smart plugs, energy monitors, composters, and e-bikes without modifying property.
Yes. Smart thermostats and plugs help reduce waste by adjusting energy use automatically.
Greywater systems, rain harvesting, and low-flow fixtures offer the highest impact.
TECHNOLOGY
Artificial Intelligence for Artists: A Practical, Human Guide to Creating Smarter (Not Soulless) Art

If you’re an artist, chances are you’ve felt it—that mix of curiosity and unease when someone mentions artificial intelligence for artists. Maybe a friend sent you an AI-generated image that looked too good. Maybe a client asked if you could “use AI to speed things up.” Or maybe you’ve quietly wondered whether these tools could actually help you break a creative block instead of replacing what you do.
I’ve been in creative rooms where AI felt like a gimmick—and in others where it genuinely unlocked new possibilities. The truth lives in the middle. Used thoughtfully, artificial intelligence for artists isn’t about cutting corners or losing your voice. It’s about expanding your toolkit, protecting your time, and giving your imagination more room to breathe.
This guide is written like a conversation between working creatives. We’ll unpack what AI really is (without jargon), how artists are using it right now, where it shines, where it fails, and how to integrate it without sacrificing authorship, ethics, or originality. By the end, you’ll know exactly how to decide if, when, and how AI belongs in your practice.
Artificial Intelligence for Artists: What It Actually Means (Without the Tech Headache)
Artificial intelligence for artists sounds intimidating because it’s often explained from a programmer’s perspective. Let’s flip that.
Think of AI less like a robot artist and more like a hyper-fast creative assistant. It doesn’t feel inspiration. It recognizes patterns—millions of them—then predicts what might come next based on your input. That’s it.
When you type a prompt into an image generator, AI isn’t “imagining” a scene. It’s statistically assembling visual elements based on what it has learned from existing images. When you use AI to upscale a sketch or generate color palettes, it’s not making aesthetic judgments—it’s applying learned probabilities.
For artists, this matters because AI is reactive, not proactive. You remain the director. The stronger your creative intent, the better the results.
In practice, artificial intelligence for artists usually falls into four categories:
- Ideation support: mood boards, rough concepts, composition variations
- Production assistance: upscaling, background generation, cleanup
- Workflow automation: tagging, resizing, exporting, batch tasks
- Exploration tools: style mixing, surreal experimentation, rapid iteration
The biggest misconception is that AI replaces skill. In reality, it amplifies skill. A trained artist gets far more value from AI than a beginner because they can spot errors, refine prompts, and shape outcomes with intention.
Why Artificial Intelligence for Artists Matters Right Now
We’re at a turning point similar to when digital art tablets first appeared. Traditional artists worried about losing craft. Digital artists worried about oversaturation. Then the dust settled—and tools became normal.
Artificial intelligence for artists matters today because:
- Creative timelines are shrinking
- Clients expect faster iteration
- Content demand has exploded across platforms
- Burnout is real, especially for freelancers
AI doesn’t remove the need for taste, judgment, or experience. It removes busywork. And in creative careers, time saved often means better art—not lazier art.
More importantly, artists who understand AI can:
- Set boundaries with clients
- Price work based on value, not hours
- Experiment without fear of wasting materials
- Stay competitive without racing to the bottom
Ignoring AI doesn’t protect your craft. Understanding it does.
Benefits and Real-World Use Cases of Artificial Intelligence for Artists


Let’s move past theory and talk about how artificial intelligence for artists is actually being used in studios, home offices, and freelance workflows.
Concept Artists and Illustrators
AI is frequently used at the sketch stage. Instead of staring at a blank canvas, artists generate rough compositions, lighting ideas, or environment concepts. These outputs aren’t final—they’re springboards.
A concept artist I worked with described AI as “visual brainstorming at warp speed.” He still painted everything himself, but he started with better questions.
Fine Artists and Mixed Media Creators
Painters and sculptors use AI to test compositions before committing materials. Photographers experiment with surreal backdrops. Installation artists map spatial ideas quickly.
AI doesn’t replace the final piece—it informs it.
Graphic Designers and Brand Artists
Designers use AI for:
- Rapid layout variations
- Background extensions
- Mockups for client approval
This reduces revision fatigue and keeps creative energy focused on strategy and storytelling.
Digital Creators and Social Artists
Artists producing content regularly—thumbnails, posters, album art—use AI to maintain consistency without burnout. AI handles repetitive variations so humans focus on narrative and emotion.
The common thread? Artificial intelligence for artists works best when it supports decision-making, not when it makes decisions for you.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Using Artificial Intelligence for Artists (Without Losing Control)


Step 1: Define Your Creative Intent First
Never open an AI tool without a goal. Are you exploring mood? Composition? Color? Texture? The clearer your intent, the more useful AI becomes.
Write a one-sentence brief like:
“I’m exploring moody lighting for a cyberpunk alley scene.”
This keeps AI outputs aligned with your vision instead of distracting you.
Step 2: Choose the Right Tool for the Job
Not all AI tools are interchangeable. Some are better for photorealism, others for illustration, others for design cleanup. We’ll compare tools in detail shortly.
Step 3: Learn Prompting Like a Visual Language
Prompting isn’t cheating—it’s communication. Artists who understand visual terminology get better results.
Instead of:
“Cool fantasy character”
Try:
“Painterly fantasy portrait, soft rim lighting, muted color palette, expressive brush strokes, shallow depth of field”
Your art education matters here.
Step 4: Iterate, Don’t Settle
The first output is rarely the best. Use AI like sketch paper. Generate variations, compare, refine.
Step 5: Take Back Control in Post-Processing
The most professional results come when artists repaint, redraw, or collage AI outputs. This is where authorship becomes clear—and defensible.
Artificial Intelligence for Artists: Tools, Comparisons, and Honest Recommendations



Midjourney
Best for expressive, painterly visuals and fast ideation. Incredible aesthetic range, but limited control unless you’re experienced with prompts.
Pros: Beautiful outputs, strong community
Cons: Less precise, subscription-based
Stable Diffusion
Ideal for artists who want control. You can train custom styles and work locally.
Pros: Customization, open-source flexibility
Cons: Steeper learning curve
Adobe Firefly
Designed with artists and licensing in mind. Integrates seamlessly with Photoshop and Illustrator.
Pros: Commercially safe, intuitive
Cons: Less experimental
Free vs Paid Tools
Free tools are great for exploration. Paid tools save time and offer reliability. Professionals usually blend both.
The best setup isn’t one tool—it’s a workflow.
Common Mistakes Artists Make with AI (and How to Fix Them)
The biggest mistake? Letting AI lead instead of follow.
Many artists:
- Skip concept development
- Accept first outputs
- Overuse trending styles
- Ignore ethical considerations
Fixes are simple but intentional:
- Always sketch or write first
- Use AI outputs as references, not finals
- Develop a recognizable personal style
- Understand usage rights and attribution
Artificial intelligence for artists rewards discernment. Taste is your competitive edge.
Ethics, Authorship, and Staying True to Your Voice
This conversation matters. Artists worry about originality—and rightly so.
Ethical use means:
- Being transparent when required
- Avoiding direct imitation of living artists’ styles
- Adding substantial human transformation
- Respecting platform licensing rules
AI doesn’t erase authorship if your creative decisions dominate the process. The line isn’t tool usage—it’s intent and transformation.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence for Artists (and Why Humans Still Matter)
AI will get faster. Outputs will get cleaner. But meaning, context, and emotional resonance remain human domains.
Audiences don’t connect with perfection. They connect with perspective.
Artists who thrive won’t be those who reject AI—or blindly adopt it—but those who use it deliberately, ethically, and creatively.
If you want a solid visual walkthrough of AI-assisted art workflows, this YouTube breakdown is genuinely helpful for artists:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2v5R4wEJbLQ
Conclusion: Artificial Intelligence for Artists Is a Tool, Not a Threat
Artificial intelligence for artists isn’t about replacing creativity—it’s about reclaiming it. When used with intention, AI frees you from repetitive labor and gives you space to think, feel, and experiment.
The artists who benefit most aren’t the fastest or loudest. They’re the ones who stay curious, grounded, and human.
Try one tool. Test one workflow. Keep your standards high. And remember: the art still begins—and ends—with you.
FAQs
No. It’s a tool. Authorship depends on how much creative control and transformation you apply.
Yes, depending on the platform’s licensing terms and your level of human contribution.
It replaces repetitive tasks, not taste, storytelling, or originality.
Purely AI-generated work often isn’t. Human-transformed work usually is.
Visual literacy, art fundamentals, and clear creative direction.
TECHNOLOGY
Brain Chip Technology: How Human Minds Are Beginning to Interface With Machines
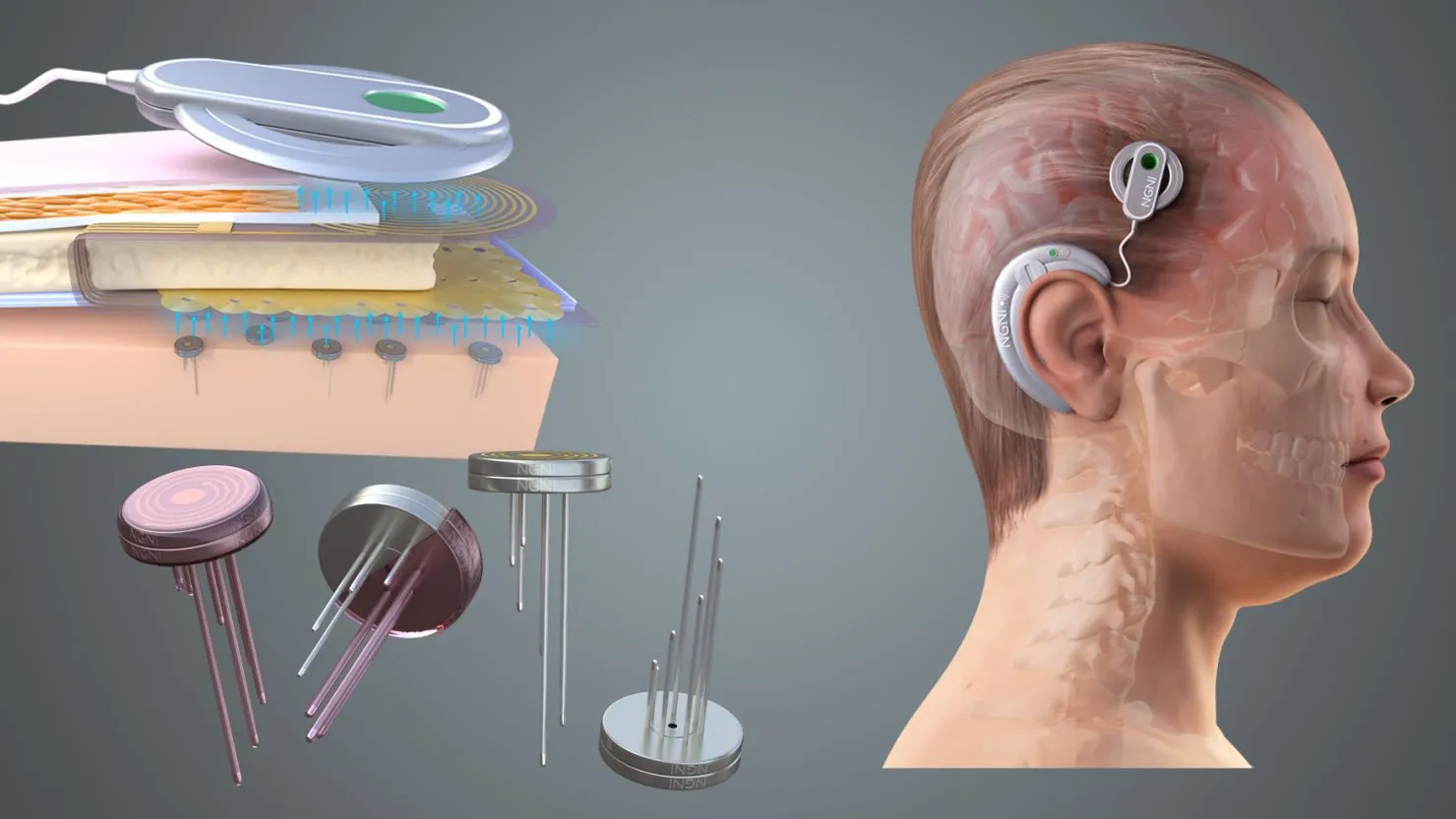
Brain chip technology is no longer a sci-fi trope whispered about in futuristic novels or late-night podcasts. It’s real, it’s advancing quickly, and it’s quietly reshaping how we think about health, ability, communication, and even what it means to be human. If you’ve ever wondered whether humans will truly connect their brains to computers—or whether that future is already here—you’re asking the right question at exactly the right time.
In the first 100 words, let’s be clear: brain chip technology refers to implantable or wearable systems that read, interpret, and sometimes stimulate neural activity to help the brain communicate directly with machines. This technology matters because it sits at the intersection of medicine, neuroscience, artificial intelligence, ethics, and human potential. In this deep-dive guide, you’ll learn how brain chips work, who they help today, where the technology is heading, the benefits and risks involved, and how to separate hype from reality.
Understanding Brain Chip Technology in Simple Terms
At its core, brain chip technology is about translating the language of the brain—electrical signals fired by neurons—into something computers can understand. Think of your brain as an incredibly fast, complex orchestra where billions of neurons communicate through electrical impulses. A brain chip acts like a highly sensitive microphone placed inside that orchestra, listening carefully and translating those signals into digital commands.
This field is more formally known as brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). Some BCIs are external, using EEG caps that sit on the scalp. Others are invasive, meaning tiny electrodes are surgically implanted into specific regions of the brain. The more closely you listen to neurons, the more accurate the signal becomes, which is why implantable brain chips are such a big focus right now.
To make this relatable, imagine typing without your hands. Instead of pressing keys, you think about moving your fingers, and the brain chip detects those intentions and converts them into text on a screen. That’s not hypothetical—it’s already happening in clinical trials. The magic lies not in reading thoughts like a mind reader, but in detecting patterns associated with intention, movement, or sensation.
The Science Behind Brain Chip Technology (Without the Jargon)
The human brain communicates using electrochemical signals. When neurons fire, they create tiny voltage changes. Brain chips use microelectrodes to detect these changes and feed the data into algorithms trained to recognize patterns.
Modern brain chip systems rely heavily on machine learning. Over time, the system “learns” what specific neural patterns mean for a particular person. This personalization is critical because no two brains are wired exactly alike.
There are three main technical components involved:
Neural sensors that capture brain activity
Signal processors that clean and decode the data
Output systems that translate signals into actions like moving a cursor or activating a prosthetic
Some advanced brain chips also work in reverse. They don’t just read signals—they send electrical stimulation back into the brain. This is how treatments like deep brain stimulation already help patients with Parkinson’s disease. The next generation aims to restore sensation, reduce chronic pain, or even repair damaged neural circuits.
Why Brain Chip Technology Matters More Than Ever
The urgency around brain chip technology isn’t about novelty—it’s about unmet needs. Millions of people worldwide live with paralysis, neurodegenerative diseases, spinal cord injuries, or speech impairments. Traditional medicine can only go so far once neural pathways are damaged.
Brain chips offer a workaround. Instead of repairing broken biological connections, they bypass them. That’s a profound shift in how we approach disability and recovery.
Beyond healthcare, the technology raises serious questions about human augmentation, cognitive enhancement, privacy, and ethics. We’re standing at the same kind of crossroads humanity faced with the internet or smartphones—except this time, the interface is the human brain itself.
Real-World Benefits and Use Cases of Brain Chip Technology
Restoring Movement and Independence
One of the most powerful applications of brain chip technology is helping paralyzed individuals regain control over their environment. People with spinal cord injuries have used brain chips to control robotic arms, wheelchairs, and even their own paralyzed limbs through external stimulators.
The emotional impact of this cannot be overstated. Being able to pick up a cup, type a message, or scratch an itch after years of immobility is life-changing. These aren’t flashy demos; they’re deeply human victories.
Communication for Locked-In Patients
Patients with ALS or brainstem strokes sometimes retain full cognitive ability but lose the power to speak or move. Brain chips allow them to communicate by translating neural signals into text or speech.
In clinical trials conducted by organizations like BrainGate, participants have typed sentences using only their thoughts. For families, this restores not just communication, but dignity and connection.
Treating Neurological Disorders
Brain chips are also being explored for treating epilepsy, depression, OCD, and chronic pain. By monitoring abnormal neural patterns and intervening in real time, these systems could offer more precise treatments than medication alone.
Unlike drugs that affect the entire brain, targeted neural stimulation focuses only on the circuits involved, reducing side effects and improving outcomes.
Future Cognitive Enhancement (With Caveats)
While medical use comes first, many people are curious about enhancement—faster learning, improved memory, or direct brain-to-AI interaction. Companies like Neuralink, founded by Elon Musk, openly discuss long-term goals involving human-AI symbiosis.
It’s important to note that enhancement applications remain speculative and ethically complex. Today’s reality is firmly medical and therapeutic.
A Practical, Step-by-Step Look at How Brain Chip Technology Is Used
Understanding the process helps demystify the technology and separate reality from hype.
The journey typically begins with patient evaluation. Neurologists determine whether a person’s condition could benefit from a brain-computer interface. Not everyone is a candidate, and risks are carefully weighed.
Next comes surgical implantation for invasive systems. Using robotic assistance and brain imaging, surgeons place microelectrodes with extreme precision. The procedure is delicate but increasingly refined.
After implantation, calibration begins. This is where machine learning plays a central role. The system observes neural activity while the user attempts specific actions, gradually learning how to interpret their signals.
Training follows. Users practice controlling devices through thought alone. This stage requires patience, but most users improve rapidly as brain and machine adapt to each other.
Ongoing monitoring and updates ensure safety and performance. In regulated environments, oversight from agencies like the FDA ensures ethical and medical compliance.
Tools, Platforms, and Leading Brain Chip Developers
Several organizations are shaping the present and future of brain chip technology.
Synchron focuses on minimally invasive implants delivered through blood vessels, avoiding open-brain surgery. Their approach reduces risk and speeds recovery.
Blackrock Neurotech provides research-grade neural implants used in many clinical trials worldwide. Their Utah Array has become a standard in neuroscience research.
Academic-industry partnerships continue to drive innovation, blending rigorous science with real-world application. While consumer versions don’t exist yet, medical systems are advancing steadily.
Free vs paid doesn’t quite apply here like it does in software, but the distinction between research access and commercial availability is important. Most current brain chip systems are accessible only through clinical trials.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions About Brain Chip Technology
One of the biggest mistakes people make is assuming brain chips can read private thoughts. They cannot. These systems decode specific neural patterns related to trained tasks, not abstract ideas or secrets.
Another misconception is that brain chip users lose autonomy or become controlled by machines. In reality, control flows from human to machine, not the other way around. The user remains fully conscious and in charge.
Many also overestimate the speed of development. While progress is impressive, widespread consumer brain chips are not imminent. Regulatory, ethical, and safety hurdles are substantial and necessary.
Finally, ignoring ethical considerations is a serious error. Data privacy, consent, and long-term effects must be addressed responsibly as the technology evolves.
Ethical, Legal, and Social Implications You Should Understand
Brain chip technology forces society to confront new ethical territory. Who owns neural data? How do we protect users from misuse? Could access become unequal?
Regulation is still catching up. Governments, ethicists, and technologists must collaborate to ensure safeguards without stifling innovation. Transparency and public dialogue are essential.
The most responsible developers emphasize medical need first, enhancement later—if ever. This prioritization builds trust and aligns innovation with genuine human benefit.
Where Brain Chip Technology Is Headed Next
The next decade will likely bring smaller implants, wireless power, longer lifespans, and improved signal resolution. Non-invasive and minimally invasive approaches will expand accessibility.
Integration with AI will improve decoding accuracy and personalization. However, meaningful breakthroughs will come from clinical success stories, not flashy announcements.
Brain chip technology won’t replace smartphones overnight, but it may quietly redefine assistive medicine and rehabilitation in ways we’re only beginning to understand.
Conclusion: What Brain Chip Technology Really Means for Humanity
Brain chip technology isn’t about turning people into cyborgs. It’s about restoring lost abilities, unlocking communication, and giving people back parts of their lives once thought gone forever. The true power of this technology lies not in futurism, but in compassion.
As research continues and safeguards mature, brain chips may become one of the most humane uses of advanced technology we’ve ever developed. If you’re curious, cautious, or cautiously optimistic—you’re in good company. The future of brain chip technology will be shaped not just by engineers, but by informed, engaged humans like you.
FAQs
Current systems are tested under strict clinical protocols. While surgery carries risk, safety has improved significantly.
No. They detect trained neural patterns related to specific tasks, not abstract or private thoughts.
People with paralysis, ALS, spinal cord injuries, and certain neurological disorders benefit most today.
Some implants are designed for long-term use, while others can be removed or upgraded.
Not yet. Most access is through clinical trials or specialized medical programs.
TECHNOLOGY
Face Recognition Technology: How It Works, Where It’s Used, and What the Future Holds

Have you ever unlocked your phone without typing a password, walked through an airport without showing your boarding pass, or noticed a camera that seems a little too smart? Behind those everyday moments is face recognition technology, quietly reshaping how we interact with devices, services, and even public spaces.
I still remember the first time I saw face recognition used outside a smartphone. It was at a corporate office where employees simply walked in—no badges, no sign-in desk. The system recognized faces in real time, logging attendance automatically. It felt futuristic… and slightly unsettling. That mix of convenience and concern is exactly why face recognition technology matters today.
This technology is no longer limited to sci-fi movies or government labs. It’s now embedded in smartphones, banking apps, airports, retail stores, healthcare systems, and even classrooms. Businesses love it for security and efficiency. Consumers love it for speed and ease. Regulators, meanwhile, are racing to keep up.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through what face recognition technology really is, how it works under the hood, where it’s being used successfully, and what mistakes to avoid if you’re considering it. I’ll also share practical tools, real-world use cases, ethical considerations, and where this rapidly evolving technology is headed next. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, business owner, or simply curious, you’ll leave with a clear, balanced understanding.
What Is Face Recognition Technology? (Explained Simply)
At its core, face recognition technology is a biometric system that identifies or verifies a person based on their facial features. Think of it like a digital version of how humans recognize each other—but powered by algorithms instead of memory.
Here’s a simple analogy:
Imagine your brain keeping a mental “map” of someone’s face—eye distance, nose shape, jawline, and overall proportions. Face recognition software does something similar, but mathematically. It converts facial characteristics into data points, creating a unique facial signature often called a faceprint.
The process usually involves three stages:
- Face Detection – The system detects a human face in an image or video.
- Feature Analysis – Key facial landmarks (eyes, nose, mouth, cheekbones) are measured.
- Matching – The extracted data is compared against stored face templates in a database.
What makes modern face recognition powerful is artificial intelligence and deep learning. Older systems struggled with lighting, angles, or facial expressions. Today’s AI-driven models improve with more data, learning to recognize faces even with glasses, masks, facial hair, or aging.
It’s also important to distinguish between face detection and face recognition. Detection simply finds a face in an image. Recognition goes a step further—it identifies who that face belongs to. Many apps use detection only, while security systems rely on full recognition.
Why Face Recognition Technology Matters Today
Face recognition technology sits at the intersection of security, convenience, and identity. In a world where digital fraud, identity theft, and data breaches are rising, traditional passwords are no longer enough. Faces, unlike passwords, can’t be forgotten or easily stolen—at least in theory.
From a business perspective, the value is clear:
- Faster authentication than PINs or cards
- Reduced fraud in banking and payments
- Improved customer experience through personalization
- Automation of manual identity checks
From a societal perspective, the stakes are higher. Face recognition can enhance public safety, but it also raises serious questions about privacy, consent, and surveillance. This dual nature is why governments, tech companies, and civil rights groups are all paying close attention.
The technology isn’t inherently good or bad—it’s how it’s used that matters. Understanding its mechanics and implications is the first step to using it responsibly.
Benefits and Real-World Use Cases of Face Recognition Technology



1. Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
One of the strongest advantages of face recognition technology is security. Banks use it to verify users during mobile transactions. Offices use it to control access to restricted areas. Even smartphones rely on facial biometrics to protect sensitive data.
Unlike passwords or access cards, faces are difficult to duplicate. When combined with liveness detection (checking that the face is real and not a photo), systems become significantly harder to fool.
2. Seamless User Experience
Convenience is where face recognition truly shines. No typing. No remembering. No physical contact. Just look at the camera.
Examples include:
- Unlocking phones and laptops
- Contactless payments
- Hotel check-ins without front desks
- Smart homes that recognize residents
For users, this feels almost magical. For businesses, it reduces friction and boosts satisfaction.
3. Attendance, Access, and Workforce Management
Companies and schools use face recognition systems to track attendance automatically. No buddy punching. No fake sign-ins. The system logs time accurately, saving administrative hours and improving accountability.
4. Healthcare and Patient Safety
Hospitals use face recognition to identify patients, access medical records quickly, and prevent identity mix-ups. In emergencies, this can save lives by ensuring the right treatment reaches the right person.
5. Law Enforcement and Public Safety
When used responsibly and legally, face recognition helps identify missing persons, suspects, and victims. However, this use case is also the most controversial due to privacy concerns—highlighting the need for strict oversight.
How Face Recognition Technology Works: Step-by-Step


Let’s break down the technical workflow in plain language.
Step 1: Image or Video Capture
The system captures an image via a camera—this could be a smartphone camera, CCTV feed, or laptop webcam. Quality matters here. Better lighting and resolution improve accuracy.
Step 2: Face Detection
Using computer vision, the system locates a face within the image. It draws a digital boundary around it, ignoring backgrounds or other objects.
Step 3: Facial Feature Extraction
This is the heart of face recognition technology. The software measures distances between facial landmarks:
- Eye spacing
- Nose width
- Jawline shape
- Lip contours
These measurements form a numerical template unique to each individual.
Step 4: Data Encoding
The facial template is converted into a mathematical representation. This data—not the raw image—is usually stored to protect privacy.
Step 5: Matching and Decision
The system compares the new face template against stored templates. If the similarity score crosses a predefined threshold, access is granted or identity confirmed.
Best Practices for Accuracy
- Use high-quality cameras
- Enable liveness detection
- Regularly update facial data
- Combine with other authentication methods for sensitive systems
Tools, Software, and Face Recognition Platforms Compared
When choosing face recognition technology, tools fall into two broad categories: consumer-level and enterprise-grade.
Free and Open-Source Options
Pros:
- Cost-effective
- Customizable
- Good for experimentation
Cons:
- Require technical expertise
- Limited support
- Not always production-ready
Best for developers and researchers testing concepts.
Paid and Enterprise Solutions
Pros:
- High accuracy
- Scalability
- Built-in compliance features
- Customer support
Cons:
- Subscription costs
- Vendor lock-in
Ideal for businesses needing reliability and legal compliance.
What to Look for When Choosing a Tool
- Accuracy across demographics
- Data security and encryption
- Compliance with privacy laws
- Integration with existing systems
There’s no “one-size-fits-all” solution. The best tool depends on your use case, budget, and ethical stance.
Common Mistakes with Face Recognition Technology (and How to Fix Them)
Even powerful technology fails when misused. Here are mistakes I’ve seen repeatedly—and how to avoid them.
Mistake 1: Ignoring Bias and Accuracy Issues
Early face recognition systems performed poorly on certain demographics. This leads to false positives and discrimination.
Fix:
Choose models trained on diverse datasets and test performance regularly.
Mistake 2: Poor Consent and Transparency
Deploying face recognition without informing users damages trust and may violate laws.
Fix:
Always provide clear notices, obtain consent, and explain data usage.
Mistake 3: Overreliance on Face Recognition Alone
No system is 100% accurate.
Fix:
Use multi-factor authentication for high-risk scenarios.
Mistake 4: Weak Data Protection
Storing facial data insecurely is a major risk.
Fix:
Encrypt data, limit retention, and restrict access.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations You Can’t Ignore
Face recognition technology deals with one of the most personal identifiers we have—our face. Misuse can lead to mass surveillance, loss of anonymity, and abuse of power.
Key ethical principles include:
- Consent – People should know and agree.
- Purpose Limitation – Use data only for stated goals.
- Accountability – Systems must be auditable.
- Fairness – Avoid bias and discrimination.
Governments worldwide are debating regulations, and businesses that ignore ethics risk backlash, fines, and reputational damage.
The Future of Face Recognition Technology
The next generation of face recognition technology will be smarter, more private, and more regulated.
Trends to watch:
- On-device processing (no cloud storage)
- Improved accuracy with masks and aging
- Stronger privacy-preserving techniques
- Integration with augmented reality and smart cities
The future isn’t about more surveillance—it’s about smarter, safer identity verification.
Conclusion
Face recognition technology is no longer a novelty—it’s a foundational tool shaping security, convenience, and digital identity. When implemented responsibly, it saves time, reduces fraud, and improves experiences. When misused, it threatens privacy and trust.
The key takeaway? Use face recognition with intention. Understand how it works, choose the right tools, respect ethics, and stay informed as regulations evolve.
If you’re exploring this technology for business or personal use, start small, test carefully, and always put people first. Technology should serve humans—not the other way around.
FAQs
Yes, when implemented with strong security, encryption, and consent-based policies.
Top systems exceed 99% accuracy in controlled conditions, though real-world performance varies.
Modern AI models can, though accuracy may slightly decrease.
It depends on your country and use case. Always check local laws.
Like any data, yes—if poorly protected. Strong security minimizes risk.
-

 HEALTH7 months ago
HEALTH7 months agoChildren’s Flonase Sensimist Allergy Relief: Review
-

 BLOG6 months ago
BLOG6 months agoDiscovering The Calamariere: A Hidden Gem Of Coastal Cuisine
-

 TECHNOLOGY6 months ago
TECHNOLOGY6 months agoHow to Build a Mobile App with Garage2Global: From Idea to Launch in 2025
-

 TECHNOLOGY2 months ago
TECHNOLOGY2 months agoAVtub: The Rise of Avatar-Driven Content in the Digital Age
-

 BLOG7 months ago
BLOG7 months agoWarmables Keep Your Lunch Warm ~ Lunch Box Kit Review {Back To School Guide}
-

 HEALTH7 months ago
HEALTH7 months agoTurkey Neck Fixes That Don’t Need Surgery
-

 BLOG6 months ago
BLOG6 months agoKeyword Optimization by Garage2Global — The Ultimate 2025 Guide
-
 EDUCATION2 months ago
EDUCATION2 months agoHCOOCH CH2 H2O: Structure, Properties, Applications, and Safety of Hydroxyethyl Formate
