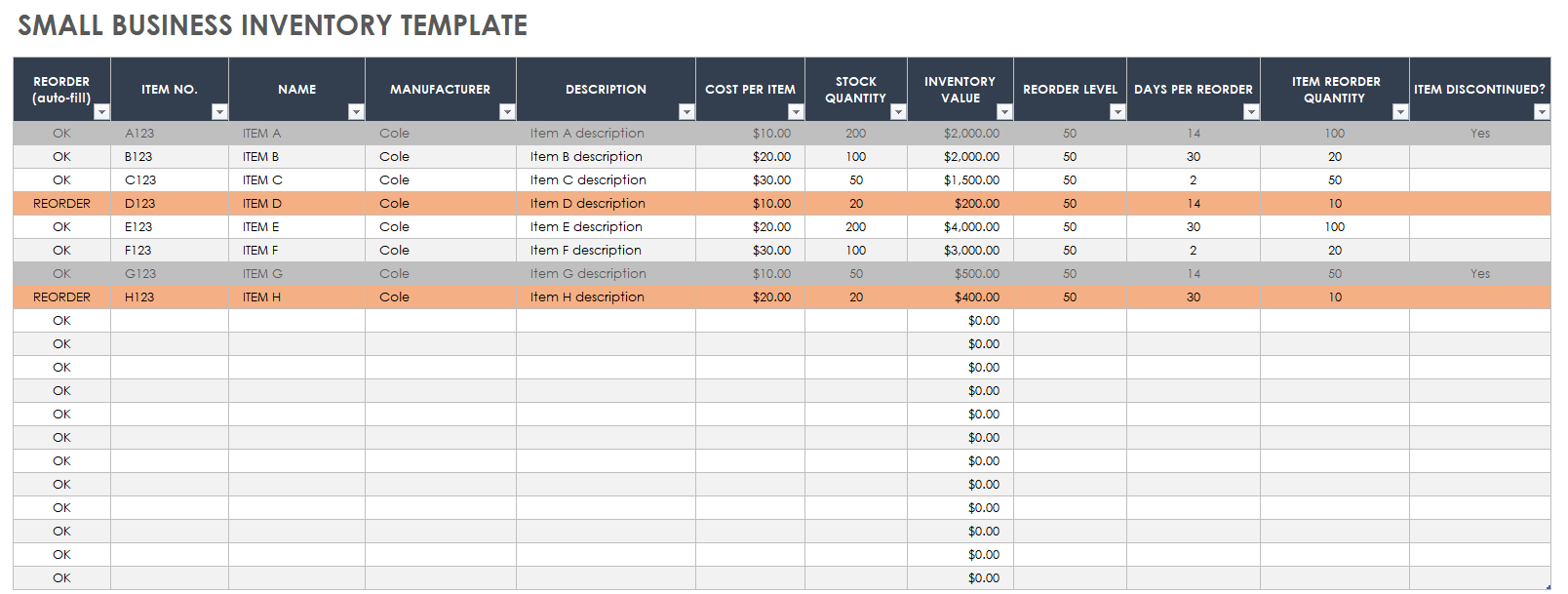
BUSINESS
3 interesting facts about chick-fil-a

Introduction
A few years ago, I was stuck in a drive-thru line that wrapped around a shopping center, spilled into a side street, and somehow still moved faster than most fast-food counters on a slow afternoon. The place? Chick-fil-A. The day? A random Tuesday. That moment sparked a simple question: how does a restaurant chain with fewer menu items, fewer operating days, and stricter franchise rules consistently outperform competitors that seem to have every possible advantage?
That curiosity is exactly why this topic matters. When people search for “3 interesting facts about Chick-fil-A,” they’re usually expecting trivia. What they often don’t realize is that these “facts” are actually strategic decisions that explain the brand’s extraordinary success.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- Why Chick-fil-A’s most criticized decisions are secretly its biggest strengths
- How the company built operational systems competitors still struggle to copy
- What its internal culture reveals about sustainable growth and trust
Whether you’re a business owner, marketer, student, or just someone who loves a good chicken sandwich, these insights will change the way you see the brand.
Topic Explanation: What People Really Mean by “3 Interesting Facts About Chick-fil-A”
At face value, “3 interesting facts about Chick-fil-A” sounds simple—almost elementary. But behind that phrase is something deeper: people are trying to understand why Chick-fil-A feels different from every other fast-food chain.
Think of it like visiting two coffee shops that sell the same drink. One feels transactional; the other feels welcoming, efficient, and oddly memorable. Chick-fil-A falls firmly into the second category, and the “interesting facts” are the clues that explain why.
These facts usually touch on three big areas:
- Operations (how they run restaurants differently)
- Culture (how they treat employees and customers)
- Strategy (how they grow while saying “no” more than “yes”)
Instead of random trivia, this guide frames each fact as a lesson. Each one shows how intentional decisions—sometimes controversial ones—can create trust, efficiency, and long-term loyalty.
In other words, these aren’t just fun facts to impress friends. They’re real-world examples of systems thinking, values-driven leadership, and brand discipline. That’s why they’re worth unpacking in detail.
Fact #1: Chick-fil-A Makes More Money Per Restaurant Than Almost Any Fast-Food Chain
This is the fact that surprises even industry insiders. Despite operating fewer days and offering a relatively limited menu, Chick-fil-A consistently leads the U.S. fast-food industry in average sales per restaurant.
To put it into perspective, many Chick-fil-A locations generate more annual revenue than McDonald’s, Starbucks, or Subway outlets—sometimes by a wide margin. And they do it with fewer items, fewer hours, and tighter operational rules.
How does that happen?
First, simplicity plays a massive role. A smaller menu means:
- Faster training for employees
- Fewer mistakes during peak hours
- More consistent food quality
Second, demand concentration is real. When you close one day a week, you don’t necessarily lose demand—you shift it. Customers adapt. Saturdays become busier. Weekdays tighten up. The brand becomes something people plan around rather than stumble into.
Third, drive-thru optimization is almost an art form at Chick-fil-A. Dual lanes, outdoor order takers, handheld POS systems, and constant experimentation mean that cars move with surprising speed. Time equals money, and Chick-fil-A respects both.
The takeaway here is simple but powerful: efficiency and focus often outperform expansion and excess. Doing fewer things exceptionally well can be more profitable than doing everything adequately.
Fact #2: Chick-fil-A Franchisees Are Chosen, Not Just Approved
If you think becoming a Chick-fil-A franchise owner is like buying into any other fast-food franchise, think again. The company famously accepts a tiny fraction of applicants—often cited as less than one percent.
Here’s what makes that interesting: the financial barrier to entry is relatively low compared to other franchises. The real barrier is trust.
Chick-fil-A doesn’t want passive investors. They want hands-on operators who treat the restaurant like a community hub. Franchisees are expected to:
- Work in the restaurant daily
- Know team members by name
- Be actively involved in local outreach
In return, Chick-fil-A offers something rare: deep operational support, strong brand equity, and a profit-sharing model that aligns incentives without encouraging shortcuts.
This model flips the traditional franchise equation. Instead of “who has the most capital,” the question becomes “who best represents the brand?”
From a business perspective, this creates consistency. From a customer perspective, it creates familiarity. And from a cultural perspective, it builds accountability at the local level.
The lesson? Growth doesn’t have to mean losing control. Sometimes the best way to scale is to slow down, choose carefully, and invest deeply in the right people.
Fact #3: Chick-fil-A’s Customer Service Is Engineered, Not Accidental
Most people chalk up Chick-fil-A’s service reputation to polite employees and friendly smiles. While that’s part of it, the truth is far more systematic.
Customer service at Chick-fil-A is designed, trained, measured, and reinforced. The famous “my pleasure” response didn’t appear by accident—it’s a cultural signal. It communicates willingness rather than obligation.
But beyond language, the systems matter:
- Employees are trained to anticipate needs, not just respond to complaints
- Managers are empowered to resolve issues on the spot
- Feedback loops ensure mistakes become learning moments
This service mindset extends to operational decisions too. For example, outdoor order takers aren’t just about speed—they create human connection. Eye contact, greetings, and small talk turn a transaction into an interaction.
What makes this fact especially interesting is how rare it is in fast food. High turnover, low margins, and pressure for speed often kill service quality. Chick-fil-A proves that when culture and systems align, service doesn’t have to be a casualty of growth.
The broader takeaway? Great service isn’t about personalities—it’s about processes that make excellence repeatable.
Benefits & Use Cases: Why These Facts Matter in the Real World
Understanding these three facts isn’t just interesting—it’s useful. They explain why Chick-fil-A dominates customer satisfaction surveys and why competitors struggle to replicate its success.
For business owners, the benefits are clear:
- Focus beats breadth when resources are limited
- Culture must be reinforced by systems, not slogans
- Selecting the right partners matters more than rapid expansion
For employees, these practices translate into:
- Clear expectations
- Stronger support structures
- Opportunities for leadership and growth
For customers, the impact is felt every visit:
- Faster service
- Consistent quality
- A sense of being valued
These use cases extend beyond restaurants. Retail stores, service businesses, startups, and even remote teams can apply the same principles: simplify operations, choose people carefully, and design experiences intentionally.
Step-by-Step Guide: Applying Chick-fil-A’s Lessons to Your Own Business or Project
You don’t need to sell chicken to learn from Chick-fil-A. Here’s a practical, step-by-step way to apply these ideas anywhere.
Step 1: Simplify Your Core Offering
Identify the 20% of products or services that deliver 80% of your results. Cut distractions. Focus there.
Step 2: Design for Peak Moments
Where do customers feel the most friction? That’s where systems matter most. Optimize those moments first.
Step 3: Hire for Values, Train for Skills
Technical skills can be taught. Attitude and alignment are harder to change.
Step 4: Create Service Scripts That Feel Human
Clear language guidelines help consistency without sounding robotic.
Step 5: Measure What Matters
Track satisfaction, repeat visits, and resolution time—not just revenue.
Each step reinforces the same idea: intentional design beats reactive management.
Tools, Comparisons & Recommendations
Chick-fil-A’s success didn’t come from flashy tech alone, but tools still matter. Comparable businesses often use:
- POS systems with real-time analytics
- Employee training platforms
- Customer feedback tools
Free tools can work at small scales, but paid platforms often offer better integration and insights. The key is alignment—tools should support your values, not override them.
Pros of Chick-fil-A’s approach:
- Consistency
- Scalability
- Strong brand trust
Cons:
- Slower expansion
- Less flexibility for franchisees
Alternatives work for some brands, but Chick-fil-A’s model excels where experience matters more than variety.
Common Mistakes & Fixes
Many businesses try to copy Chick-fil-A and fail. Common mistakes include:
- Mimicking language without changing systems
- Prioritizing speed over experience
- Scaling culture faster than people
The fix? Start small. Build systems that support behavior. Scale only when culture is stable.
Conclusion
When people ask for “3 interesting facts about Chick-fil-A,” they’re often looking for something fun. What they usually find is something far more valuable: a masterclass in focus, culture, and operational excellence.
These facts show that success doesn’t always come from doing more. Sometimes, it comes from doing less—better.
If this breakdown sparked new ideas or challenged old assumptions, take a moment to reflect on where simplicity, intention, and care could make the biggest difference in your own work or business.
FAQs
Its focus on simplicity, culture, and intentional service design sets it apart.
The decision reflects company values and reinforces work-life balance.
On a per-restaurant basis, yes—often significantly.
Extremely competitive, with acceptance rates below one percent.
Absolutely. Consistent service drives loyalty and repeat visits.

BUSINESS
Business Formal: The Complete, Real-World Guide to Dressing With Authority, Confidence, and Credibility

Introduction: Why Business Formal Still Matters (More Than You Think)
Let’s start with a truth most people won’t say out loud: business formal intimidates people.
Not because it’s complicated — but because the rules feel invisible. One wrong blazer cut, the wrong shoe polish, a slightly casual fabric, and suddenly you’re the only person in the room who feels underdressed, overdressed, or simply out of place.
Business formal isn’t just about clothes. It’s about first impressions, trust, authority, and perceived competence — all formed in seconds before you’ve spoken a word.
In high-stakes environments like executive meetings, legal settings, corporate finance, international business, or formal interviews, business formal still carries weight. It signals seriousness. It says, “I respect this room, this moment, and the people in it.”
This guide will walk you through business formal from the ground up — no fashion fluff, no outdated rules, no confusing jargon. You’ll learn what business formal really means today, how it differs by context, how to dress correctly step by step, what mistakes quietly sabotage credibility, and how to make business formal work for you instead of against you.
Whether you’re entering corporate life, leveling up your leadership presence, or simply tired of guessing — this is your definitive, practical guide.
What Is Business Formal? A Clear, Beginner-Friendly Explanation
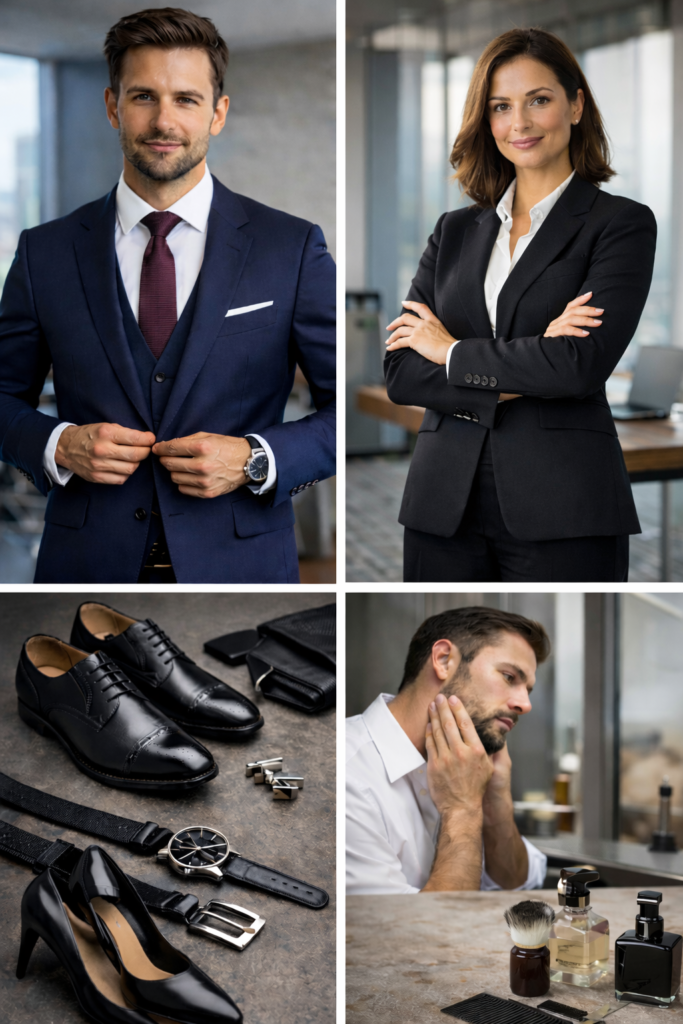

Business formal is the most conservative and polished professional dress code. It prioritizes structure, restraint, quality, and consistency over personal expression.
Think of business formal like the “grammar” of professional clothing. Just as proper grammar helps your ideas land clearly, business formal ensures your appearance doesn’t distract from your message.
At its core, business formal communicates three things:
- Professional competence
- Respect for institutional norms
- Reliability under pressure
For men, this traditionally means a tailored suit, formal dress shirt, tie, leather dress shoes, and restrained accessories. For women, it typically involves a structured suit (pantsuit or skirt suit), conservative blouse, closed-toe shoes, and minimal jewelry.
But here’s the modern nuance: business formal isn’t frozen in time. Fabrics have evolved, cuts are cleaner, and inclusivity has expanded the acceptable silhouettes — while still maintaining polish.
A useful analogy:
Business formal is like a luxury hotel lobby. It’s elegant, intentional, and calm. Nothing flashy. Nothing sloppy. Everything belongs.
Unlike business casual (which allows interpretation), business formal is about reducing uncertainty. When people see you, they shouldn’t wonder if your outfit is appropriate — it should simply register as “correct.”
Business Formal vs. Other Dress Codes (Why Confusion Happens)
One reason people struggle with business formal is because it’s often confused with other professional dress codes. Let’s clear that up.
Business formal sits at the top of the formality ladder:
- Casual – comfort-first, personal expression
- Business casual – relaxed professionalism
- Smart business / business professional – polished but flexible
- Business formal – structured, traditional, conservative
Business casual might allow knit blazers, loafers without socks, patterned dresses, or relaxed fabrics, business formal does not.
If business casual says “I’m competent and approachable,” business formal says “I’m accountable, authoritative, and here for serious outcomes.”
This distinction matters in:
- Legal environments
- Executive leadership roles
- Investor meetings
- Government or diplomatic settings
- High-level interviews
Wearing business casual where business formal is expected doesn’t make you look modern — it makes you look unaware of the room.
Benefits and Real-World Use Cases of Business Formal
Why Business Formal Still Works Psychologically
Multiple studies in workplace psychology confirm that formal attire increases perceived authority, trustworthiness, and attention to detail.
When you dress business formal:
- People interrupt you less
- Your ideas are taken more seriously
- You’re assumed to be senior or experienced
- You’re judged on substance, not appearance
This isn’t about vanity — it’s about removing friction from communication.
Who Business Formal Is Best For
Business formal is especially valuable for:
- Executives and senior managers
- Lawyers, bankers, auditors, consultants
- Job seekers in conservative industries
- Entrepreneurs pitching investors
- Professionals working internationally
It’s also ideal when:
- You’re new and need instant credibility
- Stakes are high and impressions matter
- You’re representing an organization, not just yourself
Real-Life Scenarios Where Business Formal Wins
- A junior professional wearing a sharp business formal suit commands more respect in meetings than a casually dressed senior who looks disengaged.
- In interviews, candidates dressed business formal are often remembered more clearly and perceived as more prepared.
- During negotiations, business formal subtly signals seriousness and stability.
Business formal doesn’t guarantee success — but it removes doubt.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Dress Business Formal Correctly
Step 1: Start With the Right Suit
The suit is the foundation of business formal.
For men:
- Two-piece or three-piece suit
- Solid colors: navy, charcoal, dark gray, black
- Structured shoulders, clean lines
- Minimal pattern (if any)
For women:
- Matching blazer and trousers or skirt
- Neutral tones: black, navy, gray, beige
- Tailored fit — not tight, not oversized
- Structured fabric that holds shape
Fit matters more than brand. A mid-range suit tailored properly beats an expensive ill-fitting one every time.
Step 2: Choose a Professional Shirt or Blouse
Shirts should be crisp, clean, and understated.
- White, ivory, or light blue are safest
- Avoid sheer fabrics
- Avoid loud prints or trendy cuts
- Proper sleeve and collar structure
The goal is clarity, not creativity.
Step 3: Shoes Make or Break Business Formal
Shoes are where credibility often quietly fails.
For men:
- Leather Oxford or Derby shoes
- Black or dark brown
- Polished and well-maintained
For women:
- Closed-toe heels or flats
- Neutral colors
- Stable heel height
- Clean lines, no embellishments
Scuffed shoes undermine everything else.
Step 4: Accessories Should Whisper, Not Shout
Business formal accessories are intentional and minimal.
- Conservative belts
- Classic watches
- Minimal jewelry
- Structured bags
If someone remembers your accessories more than your conversation, they were too much.
Step 5: Grooming Is Non-Negotiable
Business formal extends beyond clothing.
- Clean, styled hair
- Neutral makeup
- Trimmed facial hair
- Light or no fragrance
Presentation is part of professionalism.
Tools, Comparisons, and Smart Recommendations
Free vs. Paid Styling Help
Free tools:
- Office dress code guides
- Brand lookbooks
- Workplace observation
Paid options:
- Tailoring services
- Professional stylists
- Capsule wardrobe consultations
Ready-to-Wear vs. Custom Tailoring
Ready-to-wear:
- Faster
- Cheaper
- Limited precision
Tailored:
- Perfect fit
- Higher upfront cost
- Long-term confidence
For business formal, tailoring is often the smartest investment.
Expert Tip
Own fewer pieces, but make them exceptional. Business formal rewards consistency over variety.
Common Business Formal Mistakes (and How to Fix Them)
Mistake 1: Confusing Business Casual With Business Formal
Fix: When in doubt, go more formal. You can always remove a tie or blazer — you can’t add one later.
Mistake 2: Poor Fit
Fix: Budget for tailoring. Even minor adjustments change everything.
Mistake 3: Over-Accessorizing
Fix: Remove one accessory before leaving the house.
Mistake 4: Ignoring Shoes and Grooming
Fix: Treat shoes and grooming as part of your outfit, not an afterthought.
Mistake 5: Trend-Chasing
Fix: Business formal favors timelessness. Trends date quickly and signal instability.
The Modern Evolution of Business Formal
Business formal today is more inclusive, flexible, and realistic — but the core principles remain.
Modern business formal:
- Allows diverse body types
- Supports cultural variations
- Embraces comfort through better fabrics
- Focuses on intention over rigidity
What hasn’t changed is respect for the environment you’re in.
Conclusion: Business Formal Is a Strategic Tool, Not a Costume
Business formal isn’t about pretending to be someone you’re not.
It’s about showing up prepared, polished, and aligned with the moment.
When done right, business formal disappears — leaving only your confidence, competence, and clarity.
Master it once, and you’ll never second-guess your presence again.
If you’re building a professional wardrobe, refining your leadership image, or stepping into higher-stakes rooms — business formal is still one of the most powerful tools you can use.
FAQs
Business formal attire includes tailored suits, professional shirts or blouses, conservative shoes, and minimal accessories designed for formal professional settings.
Yes. Business formal remains essential in leadership, legal, financial, and high-level corporate environments where credibility matters.
Absolutely. Tailored pantsuits are fully accepted and widely preferred in modern business formal settings.
Minimal patterns are acceptable, but solid colors are safest and most professional.
Black is appropriate, especially in formal or executive settings, though navy and charcoal are often more versatile.
BUSINESS
Business Personal Property Insurance: The Complete, Real-World Guide for Business Owners

Introduction
Picture this for a moment. You unlock your business one morning, coffee in hand, already mentally running through the day’s to-do list. But something’s wrong. The door looks forced. Inside, the laptop you use for invoicing is gone. The POS system is missing. Shelves are half empty. In a few minutes, you realize the loss isn’t just emotional—it’s financial, operational, and potentially business-ending.
This is exactly where business personal property insurance steps in.
Most business owners spend plenty of time thinking about customers, marketing, payroll, and growth. Insurance often sits quietly in the background—until the day it suddenly becomes the most important document you own. Business personal property insurance protects the physical items your business relies on every single day, from computers and furniture to inventory and specialized equipment.
In this guide, we’re going deep. Not surface-level explanations or policy jargon copied from an insurer’s brochure, but a practical. Human explanation of how business personal property insurance really works in the real world. You’ll learn what it covers, what it doesn’t, how to choose the right limits. Common mistakes to avoid, and how to make sure you’re not underinsured when it matters most.
Whether you run a small home-based operation. A retail store, a growing agency, or a multi-location business, this article will give you the clarity and confidence to make smarter insurance decisions.
What Is Business Personal Property Insurance?
At its core, business personal property insurance covers the physical, movable items your business owns and uses to operate. Think of it as insurance for the “stuff” that makes your business functional.
A simple analogy helps here. If your building is the skeleton of your business .Business personal property is the muscle. Organs, and nervous system. Without it, the structure might still stand, but nothing works.
Business personal property typically includes:
- Office furniture (desks, chairs, shelving)
- Computers, servers, and electronics
- Tools and machinery
- Inventory and stock
- Fixtures you’ve installed but don’t permanently own
- Supplies and equipment used for daily operations
It’s usually bundled into a commercial property policy or a Business Owner’s Policy (BOP). But it can also exist as a standalone coverage depending on your setup.
One key point that confuses many people: business personal property is not the same as personal property under a homeowner’s policy. If you’re running a business from home. Your personal insurance likely offers very limited protection for business items—often capped at a low dollar amount. Business personal property insurance fills that gap.
Another important distinction is ownership and responsibility. The coverage applies to items you own, lease. Or are legally responsible for, even if they’re not physically located inside a building you own.
In short, business personal property insurance ensures that if disaster strikes—fire, theft, vandalism. Or certain weather events—you can replace what you need to keep operating, not just stare at an empty space and a pile of receipts.
Why Business Personal Property Insurance Matters More Than You Think
Many business owners underestimate how much their physical assets are worth until they’re forced to list them out. One laptop here, a printer there, shelves, signage, inventory—it adds up fast.
Let’s take a realistic example. A small digital agency with:
- 5 laptops at $1,500 each
- Office furniture worth $6,000
- Networking equipment worth $3,000
- Cameras and production gear worth $10,000
That’s over $26,000 in business personal property, and that’s before you factor in software-dependent hardware. Backup systems, or specialized tools. Now imagine replacing all of it out of pocket after a fire or break-in.
This insurance matters because:
- It protects your cash flow after a loss
- It shortens downtime after a disaster
- It can mean the difference between reopening or closing permanently
- It helps you meet lease or lender requirements
- It provides peace of mind so you can focus on growth
According to industry data, a significant percentage of small businesses that experience a major uninsured loss never reopen. It’s not the loss itself that kills the business—it’s the inability to recover quickly.
Business personal property insurance isn’t about worst-case paranoia. It’s about acknowledging that accidents, crime, and natural events don’t care how hard you’ve worked to build your business.
What Does Business Personal Property Insurance Cover?
Coverage details vary by policy, but most business personal property insurance includes protection against a defined list of “covered perils.” Understanding these is crucial.
Commonly covered events include:
- Fire and smoke damage
- Theft and burglary
- Vandalism
- Windstorms and hail (depending on location)
- Certain types of water damage (like burst pipes)
- Explosions
- Lightning damage
Covered property usually includes:
- Furniture and fixtures
- Machinery and tools
- Inventory and stock
- Computers and electronics
- Tenant improvements you paid for
- Property temporarily off-site (limited coverage)
Coverage is typically written on either a named perils basis (only listed events are covered) or special form (everything is covered unless specifically excluded). Special form coverage is broader and often worth the slightly higher cost.
It’s also important to understand valuation:
- Actual Cash Value (ACV): Replacement cost minus depreciation
- Replacement Cost Value (RCV): Cost to replace with new items of similar quality
Most seasoned business owners opt for replacement cost coverage, because depreciated payouts often fall far short of what you actually need to replace essential equipment.
What Business Personal Property Insurance Does Not Cover
Knowing exclusions is just as important as knowing coverage.
Common exclusions include:
- Flood damage (requires separate flood insurance)
- Earthquakes (requires separate endorsement or policy)
- Wear and tear or mechanical breakdown
- Employee theft (covered under crime insurance)
- Cyber incidents or data loss
- Vehicles (covered under commercial auto insurance)
- Property in transit (may require inland marine coverage)
This is where many claims disputes come from. A business owner assumes “insurance is insurance,” only to discover that a specific type of loss falls outside their policy’s scope.
For example, if your inventory is damaged due to a sewer backup, coverage may depend on whether you added a water backup endorsement. If your laptop is stolen from your car, coverage might be limited or excluded unless you have off-premises protection.
The fix is simple but often skipped: read the exclusions and endorsements carefully, or review them with an agent who explains them in plain English.
Who Needs Business Personal Property Insurance?
Short answer: almost every business that owns physical assets.
This includes:
- Retail stores with inventory and fixtures
- Restaurants with kitchen equipment
- Offices with electronics and furniture
- Contractors with tools and equipment
- Home-based businesses with professional gear
- E-commerce sellers storing inventory
- Creative professionals with cameras or studios
Even service-based businesses with “minimal” equipment often underestimate their exposure. A consultant may rely on a laptop, external drives, phone systems, and monitors—all critical to daily operations.
If your business would struggle to operate without replacing physical items, business personal property insurance isn’t optional—it’s foundational.
How Business Personal Property Insurance Works Step by Step


Understanding the process helps remove the intimidation factor.
Steps
1: Inventory your property
Start by listing everything your business owns. Walk through your space, room by room. Include quantities, approximate values, and replacement costs.
2: Determine replacement value
Ask yourself: what would it cost to buy this new today? Don’t rely on what you paid years ago.
3: Choose coverage limits
Your policy limit should reflect the total replacement cost, not a rough guess.
4: Select valuation method
Choose replacement cost over actual cash value whenever possible.
5: Add endorsements if needed
Consider off-premises coverage, higher limits for electronics, or coverage for property in transit.
6: Pay your premium
Premiums are typically affordable compared to the risk—often a few hundred dollars per year for small businesses.
7: File a claim if loss occurs
Document damage, notify your insurer promptly, and keep records of repairs or replacements.
8: Recover and rebuild
Once approved, funds are paid to help you replace property and resume operations.
The smoother this process is depends largely on how well you prepared before the loss.
Choosing the Right Coverage Limits
Underinsuring is one of the most common mistakes business owners make. They choose a low limit to save money, not realizing that partial coverage often leads to partial recovery.
Here’s a practical approach:
- Use replacement cost, not purchase price
- Include future growth buffer
- Account for seasonal inventory spikes
- Revisit limits annually
If your policy has a coinsurance clause and you’re underinsured, your claim payout may be reduced—even if the loss is smaller than your total limit. This surprises many first-time claimants.
A slightly higher limit usually costs far less than you expect and provides significantly better protection.
Business Personal Property Insurance vs Other Coverages
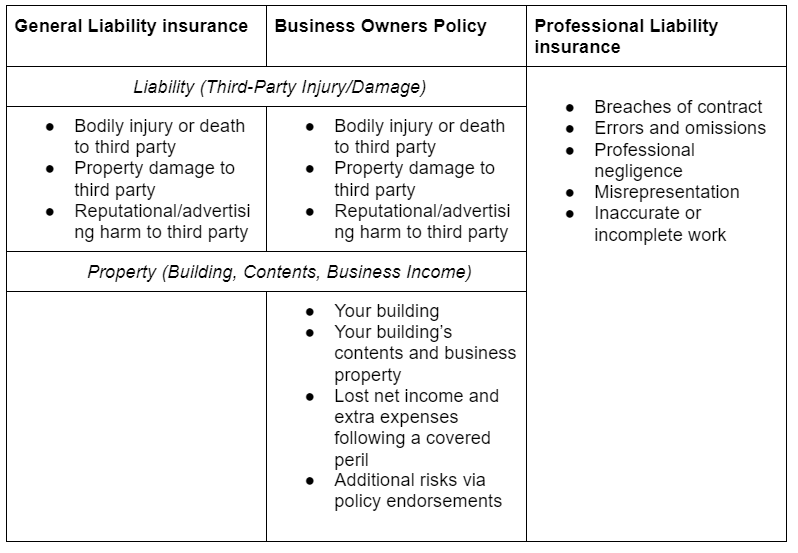
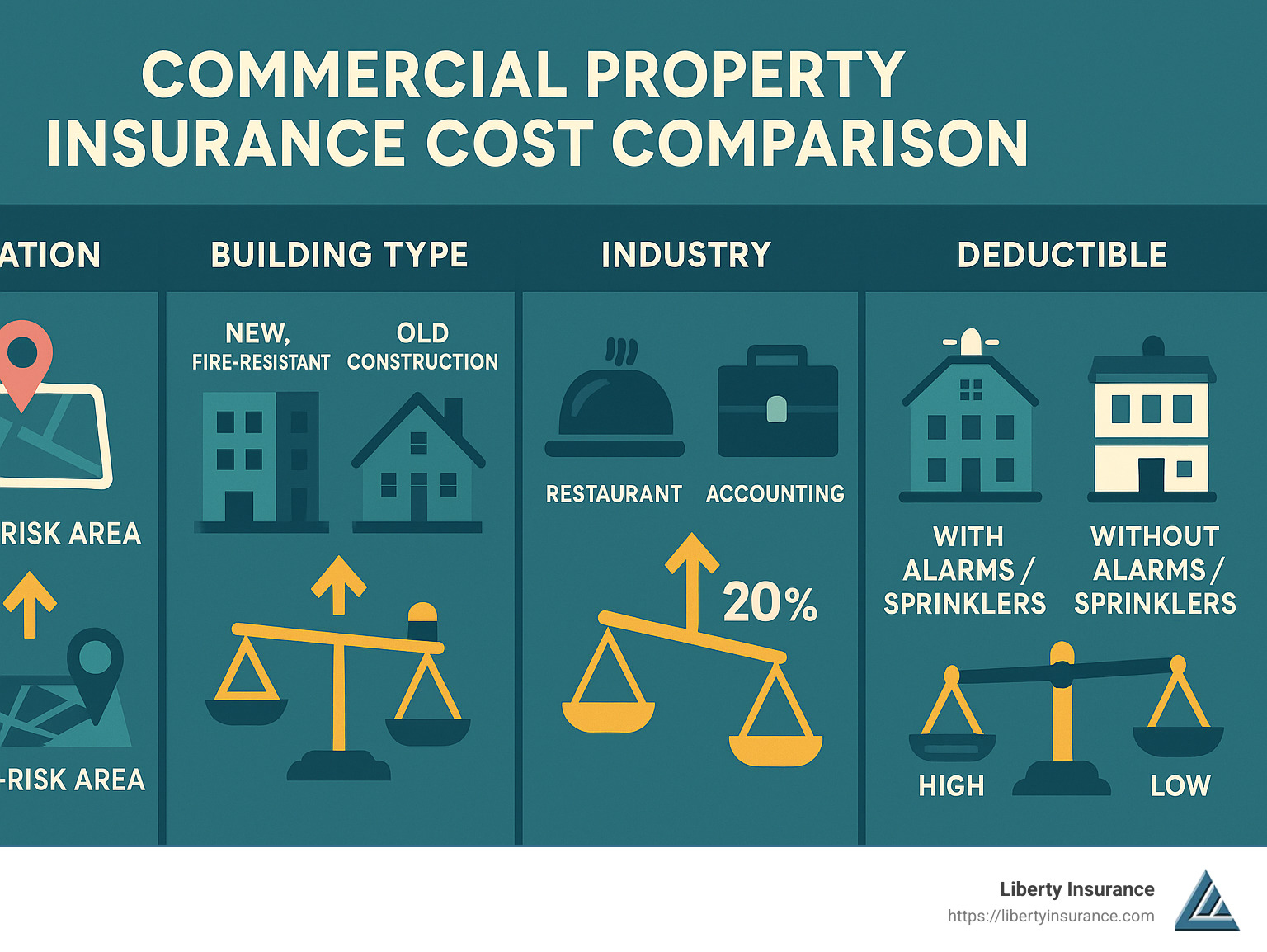
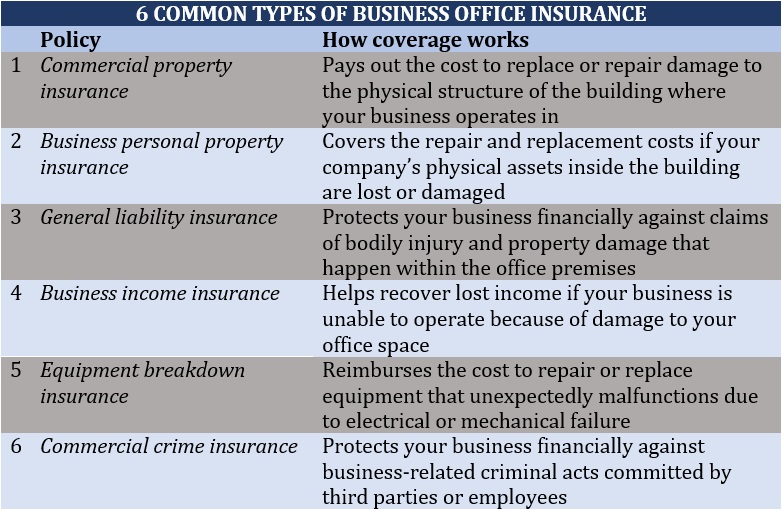
4
It helps to see how this coverage fits into the bigger picture.
Business personal property insurance:
- Covers physical items you own
- Protects against specific perils
- Focuses on replacement or repair
Commercial liability insurance:
- Covers injuries or damage to others
- Does not cover your own property
Inland marine insurance:
- Covers property in transit or off-site
- Ideal for contractors or mobile businesses
Commercial auto insurance:
- Covers vehicles and attached equipment
- Not covered under property policies
Cyber insurance:
- Covers data breaches and cyber losses
- Separate from physical property protection
Think of business personal property insurance as one piece of a well-rounded risk management puzzle.
Common Mistakes Business Owners Make (And How to Fix Them)
1: Assuming homeowner’s insurance is enough
Fix: Get a business-specific policy or endorsement.
2: Guessing coverage limits
Fix: Perform a detailed inventory and valuation.
3: Choosing actual cash value
Fix: Opt for replacement cost coverage.
4: Ignoring exclusions
Fix: Review policy details and add endorsements where needed.
5: Not updating coverage as you grow
Fix: Review annually or after major purchases.
6: Poor documentation
Fix: Keep receipts, photos, and serial numbers.
Avoiding these mistakes turns insurance from a checkbox into a true safety net.
Real-World Scenarios Where Business Personal Property Insurance Saves the Day
Scenario 1: Retail theft overnight
Inventory and POS systems are stolen. Coverage replaces equipment and stock within weeks.
Scenario 2: Office fire
Smoke and water damage destroy electronics and furniture. Replacement cost coverage allows a quick return to work.
Scenario 3: Burst pipe
Water damages inventory and fixtures. Endorsed water damage coverage covers repairs and replacements.
These aren’t rare events. They’re common stories from claims adjusters every day.
How Much Does Business Personal Property Insurance Cost?
Costs vary based on:
- Business type
- Location
- Total insured value
- Coverage form
- Deductible amount
For many small businesses, costs range from:
- $300 to $1,200 per year as part of a BOP
- More for high-risk or equipment-heavy industries
The return on investment is massive compared to the potential loss.
How to File a Successful Claim
Preparation matters more than luck.
Best practices:
- Notify your insurer immediately
- Document damage with photos and video
- Create a detailed loss inventory
- Keep damaged items until advised otherwise
- Maintain open communication
A well-documented claim moves faster and results in fewer disputes.
Conclusion
Business personal property insurance isn’t flashy. It won’t drive traffic or boost sales. But when something goes wrong—and eventually, something always does—it can be the single reason your business survives.
By understanding what it covers, choosing the right limits, avoiding common mistakes, and reviewing your policy regularly, you turn insurance from a boring expense into a powerful business continuity tool.
If you’ve ever thought, “I’ll deal with insurance later,” now is the right time to revisit that mindset. Your future self—and your business—will thank you.
FAQs
It covers physical items your business owns, such as equipment, furniture, and inventory, against covered losses.
Not usually, but landlords and lenders often require it.
Limited off-premises coverage may apply; additional coverage is often needed.
Yes, inventory is typically included, but limits and exclusions apply.
No, that requires a separate crime insurance policy.
BUSINESS
Mitch T Kloter Unlicensed Transport Business: Facts, Context, and What You Should Know

Introduction
If you’ve ever searched the phrase mitch t kloter unlicensed transport business, chances are you weren’t casually browsing. Most people don’t stumble into queries like this—they arrive with questions, concerns, or a need for clarity. Maybe you’re a consumer trying to verify legitimacy. Maybe you’re a researcher, journalist, or business professional looking to understand how unlicensed transport operations surface and why they matter. Or maybe you’re simply trying to separate fact, speculation, and misunderstanding in an industry that’s often opaque.
Transportation is one of those sectors where trust is everything. We put our safety, time, cargo, and money into the hands of operators we may never meet again. Licensing exists for a reason: it establishes accountability, safety standards, and legal oversight. When questions arise around licensing status—whether about a specific operator or a broader business model—it’s worth slowing down and examining the issue carefully rather than jumping to conclusions.
In this guide, we’ll break down what the term mitch t kloter unlicensed transport business typically signals in search intent, how unlicensed transport operations are identified, why these discussions arise, and what practical steps individuals and businesses can take to protect themselves. This article is not about accusations; it’s about understanding systems, risks, verification methods, and compliance realities—the kind of grounded, real-world insight that helps readers make informed decisions.
By the end, you’ll have a clear framework for evaluating transport businesses, understanding licensing requirements, spotting red flags, and navigating this topic with confidence rather than confusion.
Topic Explanation
To understand what people usually mean when they search mitch t kloter unlicensed transport business, it helps to first unpack how licensing works in the transport industry—and why the word “unlicensed” carries so much weight.
A licensed transport business is one that has met regulatory requirements set by local, state, or federal authorities. These requirements often include vehicle inspections, insurance coverage, driver qualifications, safety audits, and ongoing compliance reporting. Licensing isn’t just a formality; it’s a signal that an operator has passed multiple checkpoints designed to protect the public.
An “unlicensed” transport business, on the other hand, is typically defined as one operating without proper authorization for the services it provides. This doesn’t always mean malicious intent. In many real-world cases, businesses fall into gray areas—operating under the wrong classification, misunderstanding jurisdictional rules, or failing to renew permits on time. Think of it like driving with an expired license: still the same driver, still the same car, but legally non-compliant.
When a specific name becomes associated with searches like this, it often reflects public curiosity rather than proven wrongdoing. Online discussions, reviews, complaints, or regulatory inquiries can cause people to look for context. As a seasoned blogger or researcher, the responsible approach is to treat the phrase as a case-study-style keyword, not a verdict.
The key takeaway here is simple: searching this term usually means people want to understand how unlicensed transport operations are identified, what risks they pose, and how to verify legitimacy, not to consume gossip or unverified claims.
Benefits & Use Cases
You might wonder: why does understanding a phrase like mitch t kloter unlicensed transport business matter if you’re not directly involved in transportation? The answer is that the implications ripple far beyond one name or one operation.
For consumers, the benefit is protection. Knowing how licensing works allows you to verify whether a transport provider—rideshare-adjacent services, logistics operators, private carriers—is operating legally. This reduces exposure to safety risks, insurance gaps, and service disputes that are far harder to resolve when a business isn’t properly registered.
For business owners and contractors, understanding this topic helps you avoid costly partnerships. Many companies unknowingly subcontract or collaborate with transport providers who lack proper credentials. When something goes wrong, liability doesn’t stop at the driver—it can travel up the chain to whoever hired them.
Journalists, writers, and SEO professionals also benefit from this knowledge. Writing about sensitive topics requires balance. Knowing how to frame discussions around unlicensed transport activity without making claims ensures content remains credible, rankable, and legally safe.
Common real-world scenarios include:
- A customer researching a transport provider after a delayed or disputed service
- A company vetting logistics partners before signing contracts
- A regulator or compliance officer analyzing industry trends
- A blogger or publisher covering consumer safety topics responsibly
In all these cases, the goal isn’t accusation—it’s informed decision-making. Understanding the broader context empowers people to ask the right questions and take the right next steps.
Step-by-Step Guide
If you’re trying to evaluate concerns implied by searches like mitch t kloter unlicensed transport business, a structured, methodical approach works best. Guesswork and assumptions only muddy the waters.
Step one is define the service being offered. Licensing requirements vary dramatically depending on whether a business provides passenger transport, freight hauling, courier services, or private logistics. Many misunderstandings happen because people apply the wrong regulatory standard to the wrong category.
Step two is check jurisdictional requirements. Transport licensing is often layered. A business may be compliant locally but not federally, or vice versa. Understanding which authority governs the service is critical before drawing conclusions.
Step three involves verifying public records. Most legitimate transport businesses appear in licensing databases, business registries, or regulatory filings. Absence doesn’t always equal non-compliance, but it does warrant further inquiry.
Step four is review insurance and safety disclosures. Licensed operators typically carry specific insurance types and publish safety or compliance information, either publicly or upon request.
Finally, step five is evaluate patterns, not noise. One complaint or online post doesn’t define a business. Consistent reports, regulatory notices, or documented enforcement actions carry far more weight than isolated claims.
This step-by-step approach mirrors how compliance professionals and investigators actually work—slow, deliberate, evidence-based.
Tools, Comparisons & Recommendations
When researching transport business legitimacy, tools matter—but knowing which tools to trust matters even more.
Free tools like public business registries and government license lookup portals are often the first stop. They provide baseline information: registration status, permit numbers, and expiration dates. Their limitation is depth; they rarely tell the whole story.
Paid compliance platforms, on the other hand, aggregate licensing, insurance, and enforcement data across jurisdictions. These tools are commonly used by logistics firms and enterprise clients because they save time and reduce risk. The downside is cost and complexity—overkill for casual consumers.
A practical recommendation is to combine sources. Start with free public records, then cross-check with industry databases or direct documentation requests. Legitimate operators rarely object to transparency.
The biggest expert insight here is simple: no single tool gives full certainty. Credible conclusions come from cross-verification, not one screenshot or search result.
Common Mistakes & Fixes
One of the most common mistakes people make when encountering searches like mitch t kloter unlicensed transport business is assuming the keyword itself implies guilt. In reality, search behavior reflects curiosity, not court rulings.
Another frequent error is misunderstanding regulatory scope. A business might appear “unlicensed” under one authority while being fully compliant under another. Fixing this requires understanding jurisdiction, not speculation.
People also rely too heavily on online commentary. Reviews, forums, and social posts are useful signals—but they’re not evidence. The fix is simple: prioritize primary sources and official records.
Finally, many readers stop researching too early. Compliance is nuanced. Taking the extra step to verify details often changes the entire narrative.
Conclusion
The phrase mitch t kloter unlicensed transport business isn’t just a keyword—it’s a doorway into a much larger conversation about trust, regulation, and responsibility in the transport industry. Handled carelessly, topics like this can misinform. Handled correctly, they educate and empower.
By understanding how licensing works, how concerns arise, and how legitimacy is verified, you put yourself on solid ground. Whether you’re a consumer, a business owner, or a content creator, clarity beats assumption every time.
If you found this breakdown useful, consider exploring related compliance guides, sharing this with colleagues, or leaving thoughtful questions that push the discussion forward responsibly.
FAQs
It typically refers to operating transport services without the required permits for that specific service or jurisdiction.
No. Search terms reflect interest or concern, not verified conclusions.
Check official registries, request documentation, and confirm insurance coverage.
No. Requirements vary widely by region and service type.
Because transport regulations are complex and frequently updated.
-

 BLOG7 months ago
BLOG7 months agoDiscovering The Calamariere: A Hidden Gem Of Coastal Cuisine
-

 TECHNOLOGY4 months ago
TECHNOLOGY4 months agoAVtub: The Rise of Avatar-Driven Content in the Digital Age
-

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoChildren’s Flonase Sensimist Allergy Relief: Review
-

 BLOG8 months ago
BLOG8 months agoWarmables Keep Your Lunch Warm ~ Lunch Box Kit Review {Back To School Guide}
-

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoTurkey Neck Fixes That Don’t Need Surgery
-

 TECHNOLOGY7 months ago
TECHNOLOGY7 months agoHow to Build a Mobile App with Garage2Global: From Idea to Launch in 2025
-
 EDUCATION4 months ago
EDUCATION4 months agoHCOOCH CH2 H2O: Structure, Properties, Applications, and Safety of Hydroxyethyl Formate
-

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoMasago: The Tiny Sushi Topping with Big Health Benefits